What Does the Word Christmas Mean Broken Down
Holiday originating in Christianity, usually December 25
| Christmas | |
|---|---|
 Nativity scene depicted using Christmas lights | |
| Also called | Noël, Nativity, Xmas |
| Observed by | Christians, many non-Christians[1] [2] |
| Type | Christian, cultural |
| Significance | Commemoration of the nativity of Jesus |
| Celebrations | Gift-giving, family and other social gatherings, symbolic decoration, feasting etc. |
| Observances | Church services |
| Date |
|
| Frequency | Annual |
| Related to | Christmastide, Christmas Eve, Advent, Annunciation, Epiphany, Baptism of the Lord, Nativity Fast, Nativity of Christ, Old Christmas, Yule, St. Stephen's Day, Boxing Day |
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25[a] as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people around the world.[2] [10] [11] A feast central to the Christian liturgical year, it is preceded by the season of Advent or the Nativity Fast and initiates the season of Christmastide, which historically in the West lasts twelve days and culminates on Twelfth Night.[12] Christmas Day is a public holiday in many countries,[13] [14] [15] is celebrated religiously by a majority of Christians,[16] as well as culturally by many non-Christians,[1] [17] and forms an integral part of the holiday season organized around it.
The traditional Christmas narrative, the Nativity of Jesus, delineated in the New Testament says that Jesus was born in Bethlehem, in accordance with messianic prophecies.[18] When Joseph and Mary arrived in the city, the inn had no room and so they were offered a stable where the Christ Child was soon born, with angels proclaiming this news to shepherds who then spread the word.[19]
Although the month and date of Jesus' birth are unknown, the church in the early fourth century fixed the date as December 25.[20] [21] [22] This corresponds to the date of the winter solstice on the Roman calendar.[23] It is exactly nine months after Annunciation on March 25, also the date of the spring equinox. Most Christians celebrate on December 25 in the Gregorian calendar, which has been adopted almost universally in the civil calendars used in countries throughout the world. However, part of the Eastern Christian Churches celebrate Christmas on December 25 of the older Julian calendar, which currently corresponds to January 7 in the Gregorian calendar. For Christians, believing that God came into the world in the form of man to atone for the sins of humanity, rather than knowing Jesus' exact birth date, is considered to be the primary purpose in celebrating Christmas.[24] [25] [26]
The celebratory customs associated in various countries with Christmas have a mix of pre-Christian, Christian, and secular themes and origins.[27] Popular modern customs of the holiday include gift giving; completing an Advent calendar or Advent wreath; Christmas music and caroling; viewing a Nativity play; an exchange of Christmas cards; church services; a special meal; and the display of various Christmas decorations, including Christmas trees, Christmas lights, nativity scenes, garlands, wreaths, mistletoe, and holly. In addition, several closely related and often interchangeable figures, known as Santa Claus, Father Christmas, Saint Nicholas, and Christkind, are associated with bringing gifts to children during the Christmas season and have their own body of traditions and lore.[28] Because gift-giving and many other aspects of the Christmas festival involve heightened economic activity, the holiday has become a significant event and a key sales period for retailers and businesses. Over the past few centuries, Christmas has had a steadily growing economic effect in many regions of the world.
Etymology
"Christmas" is a shortened form of "Christ's mass". The word is recorded as Crīstesmæsse in 1038 and Cristes-messe in 1131.[3] Crīst (genitive Crīstes) is from Greek Khrīstos (Χριστός), a translation of Hebrew Māšîaḥ (מָשִׁיחַ), "Messiah", meaning "anointed";[29] [30] and mæsse is from Latin missa, the celebration of the Eucharist.
The form Christenmas was also historically used, but is now considered archaic and dialectal.[31] The term derives from Middle English Cristenmasse, meaning "Christian mass".[32] Xmas is an abbreviation of Christmas found particularly in print, based on the initial letter chi (Χ) in Greek Khrīstos (Χριστός), "Christ", though numerous style guides discourage its use.[33] This abbreviation has precedent in Middle English Χρ̄es masse (where "Χρ̄" is an abbreviation for Χριστός).[32]
Other names
In addition to "Christmas", the holiday has been known by various other names throughout its history. The Anglo-Saxons referred to the feast as "midwinter",[34] [35] or, more rarely, as Nātiuiteð (from Latin nātīvitās below).[34] [36] "Nativity", meaning "birth", is from Latin nātīvitās.[37] In Old English, Gēola (Yule) referred to the period corresponding to December and January, which was eventually equated with Christian Christmas.[38] "Noel" (or "Nowel") entered English in the late 14th century and is from the Old French noël or naël, itself ultimately from the Latin nātālis (diēs) meaning "birth (day)".[39]
Nativity
Gospel according to Saint Luke Chapter 2, v 1–20
The gospels of Luke and Matthew describe Jesus as being born in Bethlehem to the Virgin Mary. In Luke, Joseph and Mary travel from Nazareth to Bethlehem for the census, and Jesus is born there and laid in a manger.[40] Angels proclaimed him a savior for all people, and shepherds came to adore him.
Matthew adds that the magi follow a star to Bethlehem to bring gifts to Jesus, born the king of the Jews. King Herod orders the massacre of all the boys less than two years old in Bethlehem, but the family flees to Egypt and later returns to Nazareth.[41]
History



The nativity sequences included in the Gospels of Matthew and Luke prompted early Christian writers to suggest various dates for the anniversary.[42] Although no date is indicated in the gospels, early Christians connected Jesus to the Sun through the use of such phrases as "Sun of righteousness."[42] [43] The Romans marked the winter solstice on December 25.[23] The first recorded Christmas celebration was in Rome on December 25, AD 336.[44] [45] In the 3rd century, the date of the nativity was the subject of great interest. Around AD 200, Clement of Alexandria wrote:
There are those who have determined not only the year of our Lord's birth, but also the day; and they say that it took place in the 28th year of Augustus, and in the 25th day of [the Egyptian month] Pachon [May 20] ... Further, others say that He was born on the 24th or 25th of Pharmuthi [April 20 or 21].[46]
Various factors contributed to the selection of December 25 as a date of celebration: it was the date of the winter solstice on the Roman calendar and it was nine months after March 25, the date of the vernal equinox and a date linked to the conception of Jesus (celebrated as the Feast of the Annunciation).[47]
Christmas played a role in the Arian controversy of the fourth century. After this controversy ran its course, the prominence of the holiday declined for a few centuries. The feast regained prominence after 800 when Charlemagne was crowned emperor on Christmas Day.
In Puritan England, Christmas was banned as it was associated with drunkenness and other misbehaviour.[48] It was restored as a legal holiday in England in 1660, but remained disreputable in the minds of many people. In the early 19th century, Christmas festivities and services became widespread with the rise of the Oxford Movement in the Church of England that emphasized the centrality of Christmas in Christianity and charity to the poor,[49] along with Washington Irving, Charles Dickens, and other authors emphasizing family, children, kind-heartedness, gift-giving, and Santa Claus (for Irving),[50] or Father Christmas (for Dickens).[51]
Introduction
Christmas does not appear on the lists of festivals given by the early Christian writers Irenaeus and Tertullian.[3] Origen and Arnobius fault the pagans for celebrating birthdays, which suggests that Christmas was not celebrated in their time.[52] Arnobius wrote after AD 297. The Chronograph of 354 records that a Christmas celebration took place in Rome in 336, eight days before the calends of January.[53]
In the East, the birth of Jesus was celebrated in connection with the Epiphany on January 6.[54] [55] This holiday was not primarily about the nativity, but rather the baptism of Jesus.[56] Christmas was promoted in the East as part of the revival of Orthodox Christianity that followed the death of the pro-Arian Emperor Valens at the Battle of Adrianople in 378. The feast was introduced in Constantinople in 379, in Antioch by John Chrysostom towards the end of the fourth century,[55] probably in 388, and in Alexandria in the following century.[57]
Solstice date

Mosaic in Mausoleum M in the pre-fourth-century necropolis under St Peter's Basilica in Rome, interpreted by some as Jesus represented as Christus Sol (Christ the Sun) .[58]
December 25 was the date of the winter solstice in the Roman calendar.[23] [59] A late fourth-century sermon by Saint Augustine explains why this was a fitting day to celebrate Christ's nativity: "Hence it is that He was born on the day which is the shortest in our earthly reckoning and from which subsequent days begin to increase in length. He, therefore, who bent low and lifted us up chose the shortest day, yet the one whence light begins to increase."[60]
Linking Jesus to the Sun was supported by various Biblical passages. Jesus was considered to be the "Sun of righteousness" prophesied by Malachi: "Unto you shall the sun of righteousness arise, and healing is in his wings."[43]
Such solar symbolism could support more than one date of birth. An anonymous work known as De Pascha Computus (243) linked the idea that creation began at the spring equinox, on March 25, with the conception or birth (the word nascor can mean either) of Jesus on March 28, the day of the creation of the sun in the Genesis account. One translation reads: "O the splendid and divine providence of the Lord, that on that day, the very day, on which the sun was made, March 28, a Wednesday, Christ should be born".[3] [61]
In the 17th century, Isaac Newton, who, coincidentally, was born on December 25, argued that the date of Christmas may have been selected to correspond with the solstice.[62]
Conversely, according to Steven Hijmans of the University of Alberta, "It is cosmic symbolism ... which inspired the Church leadership in Rome to elect the southern solstice, December 25, as the birthday of Christ, and the northern solstice as that of John the Baptist, supplemented by the equinoxes as their respective dates of conception."[63]
Calculation hypothesis
The calculation hypothesis suggests that an earlier holiday held on March 25 became associated with the Incarnation.[64] Christmas was then calculated as nine months later. The calculation hypothesis was proposed by French writer Louis Duchesne in 1889.[65] [66] In modern times, March 25 is celebrated as Annunciation. This holiday was created in the seventh century and was assigned to a date that is nine months before Christmas, in addition to being the traditional date of the equinox. It is unrelated to the Quartodeciman, which had been forgotten by this time.[67] Forgotten by everyone except the Jews, of course, who continued to observe Passover; also a Quartodeciman feast.
Early Christians celebrated the life of Jesus on a date considered equivalent to 14 Nisan (Passover) on the local calendar. Because Passover was held on the 14th of the month, this feast is referred to as the Quartodeciman. All the major events of Christ's life, especially the passion, were celebrated on this date. In his letter to the Corinthians, Paul mentions Passover, presumably celebrated according to the local calendar in Corinth.[68] Tertullian (d. 220), who lived in Latin-speaking North Africa, gives the date of passion celebration as March 25.[69] The date of the passion was moved to Good Friday in 165 when Pope Soter created Easter by reassigning the Resurrection to a Sunday. According to the calculation hypothesis, the celebration of the Quartodeciman continued in some areas and the feast became associated with Incarnation.
The calculation hypothesis is considered academically to be "a thoroughly viable hypothesis", though not certain.[70] It was a traditional Jewish belief that great men were born and died on the same day, so lived a whole number of years, without fractions: Jesus was therefore considered to have been conceived on March 25, as he died on March 25, which was calculated to have coincided with 14 Nisan.[71] A passage in Commentary on the Prophet Daniel (204) by Hippolytus of Rome identifies December 25 as the date of the nativity. This passage is generally considered a late interpellation. But the manuscript includes another passage, one that is more likely to be authentic, that gives the passion as March 25.[72]
In 221, Sextus Julius Africanus (c. 160 – c. 240) gave March 25 as the day of creation and of the conception of Jesus in his universal history. This conclusion was based on solar symbolism, with March 25 the date of the equinox. As this implies a birth in December, it is sometimes claimed to be the earliest identification of December 25 as the nativity. However, Africanus was not such an influential writer that it is likely he determined the date of Christmas.[73]
The tractate De solstitia et aequinoctia conceptionis et nativitatis Domini nostri Iesu Christi et Iohannis Baptistae, pseudepigraphically attributed to John Chrysostom and dating to the early fourth century,[74] [75] also argued that Jesus was conceived and crucified on the same day of the year and calculated this as March 25.[76] [77] This anonymous tract also states: "But Our Lord, too, is born in the month of December ... the eight before the calends of January [25 December] ..., But they call it the 'Birthday of the Unconquered'. Who indeed is so unconquered as Our Lord...? Or, if they say that it is the birthday of the Sun, He is the Sun of Justice."[3]
History of religions hypothesis
The rival "History of Religions" hypothesis suggests that the Church selected December 25 date to appropriate festivities held by the Romans in honor of the Sun god Sol Invictus.[64] This cult was established by Aurelian in 274. An explicit expression of this theory appears in an annotation of uncertain date added to a manuscript of a work by 12th-century Syrian bishop Jacob Bar-Salibi. The scribe who added it wrote:
It was a custom of the Pagans to celebrate on the same 25 December the birthday of the Sun, at which they kindled lights in token of festivity. In these solemnities and revelries, the Christians also took part. Accordingly, when the doctors of the Church perceived that the Christians had a leaning to this festival, they took counsel and resolved that the true Nativity should be solemnised on that day.[78]
In 1743, German Protestant Paul Ernst Jablonski argued Christmas was placed on December 25 to correspond with the Roman solar holiday Dies Natalis Solis Invicti and was therefore a "paganization" that debased the true church.[79] However, it has been also argued that, on the contrary, the Emperor Aurelian, who in 274 instituted the holiday of the Dies Natalis Solis Invicti, did so partly as an attempt to give a pagan significance to a date already important for Christians in Rome.[80]
Hermann Usener[81] and others[3] proposed that the Christians chose this day because it was the Roman feast celebrating the birthday of Sol Invictus. Modern scholar S. E. Hijmans, however, states that "While they were aware that pagans called this day the 'birthday' of Sol Invictus, this did not concern them and it did not play any role in their choice of date for Christmas."[63] Moreover, Thomas J. Talley holds that the Roman Emperor Aurelian placed a festival of Sol Invictus on December 25 in order to compete with the growing rate of the Christian Church, which had already been celebrating Christmas on that date first.[82] In the judgement of the Church of England Liturgical Commission, the History of Religions hypothesis has been challenged[83] by a view based on an old tradition, according to which the date of Christmas was fixed at nine months after March 25, the date of the vernal equinox, on which the Annunciation was celebrated.[76]
With regard to a December religious feast of the deified Sun (Sol), as distinct from a solstice feast of the birth (or rebirth) of the astronomical sun, Hijmans has commented that "while the winter solstice on or around December 25 was well established in the Roman imperial calendar, there is no evidence that a religious celebration of Sol on that day antedated the celebration of Christmas".[84] "Thomas Talley has shown that, although the Emperor Aurelian's dedication of a temple to the sun god in the Campus Martius (C.E. 274) probably took place on the 'Birthday of the Invincible Sun' on December 25, the cult of the sun in pagan Rome ironically did not celebrate the winter solstice nor any of the other quarter-tense days, as one might expect."[85] The Oxford Companion to Christian Thought remarks on the uncertainty about the order of precedence between the religious celebrations of the Birthday of the Unconquered Sun and of the birthday of Jesus, stating that the hypothesis that December 25 was chosen for celebrating the birth of Jesus on the basis of the belief that his conception occurred on March 25 "potentially establishes 25 December as a Christian festival before Aurelian's decree, which, when promulgated, might have provided for the Christian feast both opportunity and challenge".[86]
Relation to concurrent celebrations
Many popular customs associated with Christmas developed independently of the commemoration of Jesus' birth, with some claiming that certain elements have origins in pre-Christian festivals that were celebrated by pagan populations who were later converted to Christianity. The prevailing atmosphere of Christmas has also continually evolved since the holiday's inception, ranging from a sometimes raucous, drunken, carnival-like state in the Middle Ages,[87] to a tamer family-oriented and children-centered theme introduced in a 19th-century transformation.[88] [89] The celebration of Christmas was banned on more than one occasion within certain groups, such as the Puritans and Jehovah's Witnesses (who do not celebrate birthdays in general), due to concerns that it was too unbiblical.[90] [48] [91]
Prior to and through the early Christian centuries, winter festivals were the most popular of the year in many European pagan cultures. Reasons included the fact that less agricultural work needed to be done during the winter, as well as an expectation of better weather as spring approached.[92] Celtic winter herbs such as mistletoe and ivy, and the custom of kissing under a mistletoe, are common in modern Christmas celebrations in the English-speaking countries.
The pre-Christian Germanic peoples—including the Anglo-Saxons and the Norse—celebrated a winter festival called Yule, held in the late December to early January period, yielding modern English yule, today used as a synonym for Christmas.[93] In Germanic language-speaking areas, numerous elements of modern Christmas folk custom and iconography may have originated from Yule, including the Yule log, Yule boar, and the Yule goat.[94] [93] Often leading a ghostly procession through the sky (the Wild Hunt), the long-bearded god Odin is referred to as "the Yule one" and "Yule father" in Old Norse texts, while other gods are referred to as "Yule beings".[95] On the other hand, as there are no reliable existing references to a Christmas log prior to the 16th century, the burning of the Christmas block may have been an early modern invention by Christians unrelated to the pagan practice.[96]
In eastern Europe also, old pagan traditions were incorporated into Christmas celebrations, an example being the Koleda,[97] which was incorporated into the Christmas carol.
Post-classical history

The Nativity, from a 14th-century Missal; a liturgical book containing texts and music necessary for the celebration of Mass throughout the year
In the Early Middle Ages, Christmas Day was overshadowed by Epiphany, which in western Christianity focused on the visit of the magi. But the medieval calendar was dominated by Christmas-related holidays. The forty days before Christmas became the "forty days of St. Martin" (which began on November 11, the feast of St. Martin of Tours), now known as Advent.[87] In Italy, former Saturnalian traditions were attached to Advent.[87] Around the 12th century, these traditions transferred again to the Twelve Days of Christmas (December 25 – January 5); a time that appears in the liturgical calendars as Christmastide or Twelve Holy Days.[87]
The prominence of Christmas Day increased gradually after Charlemagne was crowned Emperor on Christmas Day in 800. King Edmund the Martyr was anointed on Christmas in 855 and King William I of England was crowned on Christmas Day 1066.

The coronation of Charlemagne on Christmas of 800 helped promote the popularity of the holiday
By the High Middle Ages, the holiday had become so prominent that chroniclers routinely noted where various magnates celebrated Christmas. King Richard II of England hosted a Christmas feast in 1377 at which twenty-eight oxen and three hundred sheep were eaten.[87] The Yule boar was a common feature of medieval Christmas feasts. Caroling also became popular, and was originally performed by a group of dancers who sang. The group was composed of a lead singer and a ring of dancers that provided the chorus. Various writers of the time condemned caroling as lewd, indicating that the unruly traditions of Saturnalia and Yule may have continued in this form.[87] "Misrule"—drunkenness, promiscuity, gambling—was also an important aspect of the festival. In England, gifts were exchanged on New Year's Day, and there was special Christmas ale.[87]
Christmas during the Middle Ages was a public festival that incorporated ivy, holly, and other evergreens.[98] Christmas gift-giving during the Middle Ages was usually between people with legal relationships, such as tenant and landlord.[98] The annual indulgence in eating, dancing, singing, sporting, and card playing escalated in England, and by the 17th century the Christmas season featured lavish dinners, elaborate masques, and pageants. In 1607, King James I insisted that a play be acted on Christmas night and that the court indulge in games.[99] It was during the Reformation in 16th–17th-century Europe that many Protestants changed the gift bringer to the Christ Child or Christkindl, and the date of giving gifts changed from December 6 to Christmas Eve.[100]
Modern history
Associating it with drunkenness and other misbehaviour, the Puritans banned Christmas in England in the 17th century.[48] It was restored as a legal holiday in 1660, but remained disreputable. In the early 19th century, the Oxford Movement in the Anglican Church ushered in "the development of richer and more symbolic forms of worship, the building of neo-Gothic churches, and the revival and increasing centrality of the keeping of Christmas itself as a Christian festival" as well as "special charities for the poor" in addition to "special services and musical events".[49] Charles Dickens and other writers helped in this revival of the holiday by "changing consciousness of Christmas and the way in which it was celebrated" as they emphasized family, religion, gift-giving, and social reconciliation as opposed to the historic revelry common in some places.[49]
18th century
Following the Protestant Reformation, many of the new denominations, including the Anglican Church and Lutheran Church, continued to celebrate Christmas.[101] In 1629, the Anglican poet John Milton penned On the Morning of Christ's Nativity, a poem that has since been read by many during Christmastide.[102] [103] Donald Heinz, a professor at California State University, states that Martin Luther "inaugurated a period in which Germany would produce a unique culture of Christmas, much copied in North America."[104] Among the congregations of the Dutch Reformed Church, Christmas was celebrated as one of the principal evangelical feasts.[105]
However, in 17th century England, some groups such as the Puritans strongly condemned the celebration of Christmas, considering it a Catholic invention and the "trappings of popery" or the "rags of the Beast".[48] In contrast, the established Anglican Church "pressed for a more elaborate observance of feasts, penitential seasons, and saints' days. The calendar reform became a major point of tension between the Anglican party and the Puritan party."[106] The Catholic Church also responded, promoting the festival in a more religiously oriented form. King Charles I of England directed his noblemen and gentry to return to their landed estates in midwinter to keep up their old-style Christmas generosity.[99] Following the Parliamentarian victory over Charles I during the English Civil War, England's Puritan rulers banned Christmas in 1647.[48] [107]
Protests followed as pro-Christmas rioting broke out in several cities and for weeks Canterbury was controlled by the rioters, who decorated doorways with holly and shouted royalist slogans.[48] The book, The Vindication of Christmas (London, 1652), argued against the Puritans, and makes note of Old English Christmas traditions, dinner, roast apples on the fire, card playing, dances with "plow-boys" and "maidservants", old Father Christmas and carol singing.[108]

The Examination and Trial of Father Christmas, (1686), published after Christmas was reinstated as a holy day in England
The Restoration of King Charles II in 1660 ended the ban, but many Calvinist clergymen still disapproved of Christmas celebration. As such, in Scotland, the Presbyterian Church of Scotland discouraged the observance of Christmas, and though James VI commanded its celebration in 1618, attendance at church was scant.[109] The Parliament of Scotland officially abolished the observance of Christmas in 1640, claiming that the church had been "purged of all superstitious observation of days".[110] It was not until 1958 that Christmas again became a Scottish public holiday.[111]
Following the Restoration of Charles II, Poor Robin's Almanack contained the lines: "Now thanks to God for Charles return, / Whose absence made old Christmas mourn. / For then we scarcely did it know, / Whether it Christmas were or no."[112] The diary of James Woodforde, from the latter half of the 18th century, details the observance of Christmas and celebrations associated with the season over a number of years.[113]
In Colonial America, the Pilgrims of New England shared radical Protestant disapproval of Christmas.[91] The Plymouth Pilgrims put their loathing for the day into practice in 1620 when they spent their first Christmas Day in the New World working – thus demonstrating their complete contempt for the day.[91] Non-Puritans in New England deplored the loss of the holidays enjoyed by the laboring classes in England.[114] Christmas observance was outlawed in Boston in 1659.[91] The ban by the Puritans was revoked in 1681 by English governor Edmund Andros, however it was not until the mid-19th century that celebrating Christmas became fashionable in the Boston region.[115]
At the same time, Christian residents of Virginia and New York observed the holiday freely. Pennsylvania German Settlers, pre-eminently the Moravian settlers of Bethlehem, Nazareth and Lititz in Pennsylvania and the Wachovia Settlements in North Carolina, were enthusiastic celebrators of Christmas. The Moravians in Bethlehem had the first Christmas trees in America as well as the first Nativity Scenes.[116] Christmas fell out of favor in the United States after the American Revolution, when it was considered an English custom.[117] George Washington attacked Hessian (German) mercenaries on the day after Christmas during the Battle of Trenton on December 26, 1776, Christmas being much more popular in Germany than in America at this time.
With the atheistic Cult of Reason in power during the era of Revolutionary France, Christian Christmas religious services were banned and the three kings cake was renamed the "equality cake" under anticlerical government policies.[118] [119]
19th century

In the UK, Christmas Day became a bank holiday in 1834. Boxing Day, the day after Christmas, was added in 1871.[120]
In the early-19th century, writers imagined Tudor Christmas as a time of heartfelt celebration. In 1843, Charles Dickens wrote the novel A Christmas Carol, which helped revive the "spirit" of Christmas and seasonal merriment.[88] [89] Its instant popularity played a major role in portraying Christmas as a holiday emphasizing family, goodwill, and compassion.[50]
Dickens sought to construct Christmas as a family-centered festival of generosity, linking "worship and feasting, within a context of social reconciliation."[121] Superimposing his humanitarian vision of the holiday, in what has been termed "Carol Philosophy",[122] Dickens influenced many aspects of Christmas that are celebrated today in Western culture, such as family gatherings, seasonal food and drink, dancing, games, and a festive generosity of spirit.[123] A prominent phrase from the tale, "Merry Christmas", was popularized following the appearance of the story.[124] This coincided with the appearance of the Oxford Movement and the growth of Anglo-Catholicism, which led a revival in traditional rituals and religious observances.[125]

The Queen's Christmas tree at Windsor Castle, published in the Illustrated London News, 1848
The term Scrooge became a synonym for miser, with "Bah! Humbug!" dismissive of the festive spirit.[126] In 1843, the first commercial Christmas card was produced by Sir Henry Cole.[127] The revival of the Christmas Carol began with William Sandys's "Christmas Carols Ancient and Modern" (1833), with the first appearance in print of "The First Noel", "I Saw Three Ships", "Hark the Herald Angels Sing" and "God Rest Ye Merry, Gentlemen", popularized in Dickens' A Christmas Carol.
In Britain, the Christmas tree was introduced in the early 19th century by the German-born Queen Charlotte. In 1832, the future Queen Victoria wrote about her delight at having a Christmas tree, hung with lights, ornaments, and presents placed round it.[128] After her marriage to her German cousin Prince Albert, by 1841 the custom became more widespread throughout Britain.[129]
An image of the British royal family with their Christmas tree at Windsor Castle created a sensation when it was published in the Illustrated London News in 1848. A modified version of this image was published in Godey's Lady's Book, Philadelphia in 1850.[130] [131] By the 1870s, putting up a Christmas tree had become common in America.[130]
In America, interest in Christmas had been revived in the 1820s by several short stories by Washington Irving which appear in his The Sketch Book of Geoffrey Crayon, Gent. and "Old Christmas". Irving's stories depicted harmonious warm-hearted English Christmas festivities he experienced while staying in Aston Hall, Birmingham, England, that had largely been abandoned,[132] and he used the tract Vindication of Christmas (1652) of Old English Christmas traditions, that he had transcribed into his journal as a format for his stories.[99]

In 1822, Clement Clarke Moore wrote the poem A Visit From St. Nicholas (popularly known by its first line: Twas the Night Before Christmas).[133] The poem helped popularize the tradition of exchanging gifts, and seasonal Christmas shopping began to assume economic importance.[134] This also started the cultural conflict between the holiday's spiritual significance and its associated commercialism that some see as corrupting the holiday. In her 1850 book The First Christmas in New England, Harriet Beecher Stowe includes a character who complains that the true meaning of Christmas was lost in a shopping spree.[135]
While the celebration of Christmas was not yet customary in some regions in the U.S., Henry Wadsworth Longfellow detected "a transition state about Christmas here in New England" in 1856. "The old puritan feeling prevents it from being a cheerful, hearty holiday; though every year makes it more so."[136] In Reading, Pennsylvania, a newspaper remarked in 1861, "Even our presbyterian friends who have hitherto steadfastly ignored Christmas—threw open their church doors and assembled in force to celebrate the anniversary of the Savior's birth."[136]
The First Congregational Church of Rockford, Illinois, "although of genuine Puritan stock", was 'preparing for a grand Christmas jubilee', a news correspondent reported in 1864.[136] By 1860, fourteen states including several from New England had adopted Christmas as a legal holiday.[137] In 1875, Louis Prang introduced the Christmas card to Americans. He has been called the "father of the American Christmas card".[138] On June 28, 1870, Christmas was formally declared a United States federal holiday.[139]
20th century
Up to the 1950s in the UK, many Christmas customs were restricted to the upper classes and better-off families. The mass of the population had not adopted many of the Christmas rituals that later became general. The Christmas tree was rare. Christmas dinner might be beef or goose – certainly not turkey. In their stockings children might get an apple, orange, and sweets. Full celebration of a family Christmas with all the trimmings only became widespread with increased prosperity from the 1950s.[140] National papers were published on Christmas Day until 1912. Post was still delivered on Christmas Day until 1961. League football matches continued in Scotland until the 1970s while in England they ceased at the end of the 1950s.[141] [142]

The Christmas Visit. Postcard, c.1910
Under the state atheism of the Soviet Union, after its foundation in 1917, Christmas celebrations—along with other Christian holidays—were prohibited in public.[143] During the 1920s, '30s, and '40s, the League of Militant Atheists encouraged school pupils to campaign against Christmas traditions, such as the Christmas tree, as well as other Christian holidays, including Easter; the League established an antireligious holiday to be the 31st of each month as a replacement.[144] At the height of this persecution, in 1929, on Christmas Day, children in Moscow were encouraged to spit on crucifixes as a protest against the holiday.[145] It was not until the dissolution of the Soviet Union in 1991 that the persecution ended and Orthodox Christmas became a state holiday again for the first time in Russia after seven decades.[146]
European History Professor Joseph Perry wrote that likewise, in Nazi Germany, "because Nazi ideologues saw organized religion as an enemy of the totalitarian state, propagandists sought to deemphasize—or eliminate altogether—the Christian aspects of the holiday" and that "Propagandists tirelessly promoted numerous Nazified Christmas songs, which replaced Christian themes with the regime's racial ideologies."[147]
As Christmas celebrations began to be held around the world even outside traditional Christian cultures in the 20th century, some Muslim-majority countries subsequently banned the practice of Christmas, claiming it undermines Islam.[148]
Observance and traditions

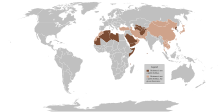
Dark brown – countries that do not recognize Christmas on December 25 or January 7 as a public holiday.
Light brown – countries that do not recognize Christmas as a public holiday, but the holiday is given observance.

Christmas Day is celebrated as a major festival and public holiday in countries around the world, including many whose populations are mostly non-Christian. In some non-Christian areas, periods of former colonial rule introduced the celebration (e.g. Hong Kong); in others, Christian minorities or foreign cultural influences have led populations to observe the holiday. Countries such as Japan, where Christmas is popular despite there being only a small number of Christians, have adopted many of the secular aspects of Christmas, such as gift-giving, decorations, and Christmas trees.
Among countries with a strong Christian tradition, a variety of Christmas celebrations have developed that incorporate regional and local cultures.
Church attendance
Christmas Day (inclusive of its vigil, Christmas Eve), is a Festival in the Lutheran Churches, a holy day of obligation in the Roman Catholic Church, and a Principal Feast of the Anglican Communion. Other Christian denominations do not rank their feast days but nevertheless place importance on Christmas Eve/Christmas Day, as with other Christian feasts like Easter, Ascension Day, and Pentecost.[150] As such, for Christians, attending a Christmas Eve or Christmas Day church service plays an important part in the recognition of the Christmas season. Christmas, along with Easter, is the period of highest annual church attendance. A 2010 survey by LifeWay Christian Resources found that six in ten Americans attend church services during this time.[151] In the United Kingdom, the Church of England reported an estimated attendance of 2.5 million people at Christmas services in 2015.[152]
Decorations

A typical Neapolitan presepe or presepio, or Nativity scene. Local crèches are renowned for their ornate decorations and symbolic figurines, often mirroring daily life.
Nativity scenes are known from 10th-century Rome. They were popularised by Saint Francis of Assisi from 1223, quickly spreading across Europe.[153] Different types of decorations developed across the Christian world, dependent on local tradition and available resources, and can vary from simple representations of the crib to far more elaborate sets – renowned manger scene traditions include the colourful Kraków szopka in Poland,[154] which imitate Kraków's historical buildings as settings, the elaborate Italian presepi (Neapolitan, Genoese and Bolognese),[155] [156] [157] [158] or the Provençal crèches in southern France, using hand-painted terracotta figurines called santons.[159] In certain parts of the world, notably Sicily, living nativity scenes following the tradition of Saint Francis are a popular alternative to static crèches.[160] [161] [162] The first commercially produced decorations appeared in Germany in the 1860s, inspired by paper chains made by children.[163] In countries where a representation of the Nativity scene is very popular, people are encouraged to compete and create the most original or realistic ones. Within some families, the pieces used to make the representation are considered a valuable family heirloom.[ citation needed ]
The traditional colors of Christmas decorations are red, green, and gold.[164] [165] Red symbolizes the blood of Jesus, which was shed in his crucifixion, while green symbolizes eternal life, and in particular the evergreen tree, which does not lose its leaves in the winter, and gold is the first color associated with Christmas, as one of the three gifts of the Magi, symbolizing royalty.[166]

The official White House Christmas tree for 1962, displayed in the Entrance Hall and presented by John F. Kennedy and his wife Jackie.
The Christmas tree was first used by German Lutherans in the 16th century, with records indicating that a Christmas tree was placed in the Cathedral of Strassburg in 1539, under the leadership of the Protestant Reformer, Martin Bucer.[167] [168] In the United States, these "German Lutherans brought the decorated Christmas tree with them; the Moravians put lighted candles on those trees."[169] [170] When decorating the Christmas tree, many individuals place a star at the top of the tree symbolizing the Star of Bethlehem, a fact recorded by The School Journal in 1897.[171] [172] Professor David Albert Jones of Oxford University writes that in the 19th century, it became popular for people to also use an angel to top the Christmas tree in order to symbolize the angels mentioned in the accounts of the Nativity of Jesus.[173] The Christmas tree is considered by some as Christianisation of pagan tradition and ritual surrounding the Winter Solstice, which included the use of evergreen boughs, and an adaptation of pagan tree worship;[174] according to eighth-century biographer Æddi Stephanus, Saint Boniface (634–709), who was a missionary in Germany, took an ax to an oak tree dedicated to Thor and pointed out a fir tree, which he stated was a more fitting object of reverence because it pointed to heaven and it had a triangular shape, which he said was symbolic of the Trinity.[175] The English language phrase "Christmas tree" is first recorded in 1835[176] and represents an importation from the German language.[174] [177] [178]

Since the 16th century, the poinsettia, a native plant from Mexico, has been associated with Christmas carrying the Christian symbolism of the Star of Bethlehem; in that country it is known in Spanish as the Flower of the Holy Night.[179] [180] Other popular holiday plants include holly, mistletoe, red amaryllis, and Christmas cactus.[181]
Other traditional decorations include bells, candles, candy canes, stockings, wreaths, and angels. Both the displaying of wreaths and candles in each window are a more traditional Christmas display.[182] The concentric assortment of leaves, usually from an evergreen, make up Christmas wreaths and are designed to prepare Christians for the Advent season. Candles in each window are meant to demonstrate the fact that Christians believe that Jesus Christ is the ultimate light of the world.[183]
Christmas lights and banners may be hung along streets, music played from speakers, and Christmas trees placed in prominent places.[184] It is common in many parts of the world for town squares and consumer shopping areas to sponsor and display decorations. Rolls of brightly colored paper with secular or religious Christmas motifs are manufactured for the purpose of wrapping gifts. In some countries, Christmas decorations are traditionally taken down on Twelfth Night.[185]
Nativity play

For the Christian celebration of Christmas, the viewing of the Nativity play is one of the oldest Christmastime traditions, with the first reenactment of the Nativity of Jesus taking place in A.D. 1223.[186] In that year, Francis of Assisi assembled a Nativity scene outside of his church in Italy and children sung Christmas carols celebrating the birth of Jesus.[186] Each year, this grew larger and people travelled from afar to see Francis' depiction of the Nativity of Jesus that came to feature drama and music.[186] Nativity plays eventually spread throughout all of Europe, where they remain popular. Christmas Eve and Christmas Day church services often came to feature Nativity plays, as did schools and theatres.[186] In France, Germany, Mexico and Spain, Nativity plays are often reenacted outdoors in the streets.[186]
Music and carols

The earliest extant specifically Christmas hymns appear in fourth-century Rome. Latin hymns such as "Veni redemptor gentium", written by Ambrose, Archbishop of Milan, were austere statements of the theological doctrine of the Incarnation in opposition to Arianism. "Corde natus ex Parentis" ("Of the Father's love begotten") by the Spanish poet Prudentius (d. 413) is still sung in some churches today.[187] In the 9th and 10th centuries, the Christmas "Sequence" or "Prose" was introduced in North European monasteries, developing under Bernard of Clairvaux into a sequence of rhymed stanzas. In the 12th century the Parisian monk Adam of St. Victor began to derive music from popular songs, introducing something closer to the traditional Christmas carol.[ citation needed ]

The songs now known specifically as carols were originally communal folk songs sung during celebrations such as "harvest tide" as well as Christmas. It was only later that carols began to be sung in church. Traditionally, carols have often been based on medieval chord patterns, and it is this that gives them their uniquely characteristic musical sound. Some carols like "Personent hodie", "Good King Wenceslas", and "The Holly and the Ivy" can be traced directly back to the Middle Ages. They are among the oldest musical compositions still regularly sung. "Adeste Fideles" (O Come all ye faithful) appears in its current form in the mid-18th century, although the words may have originated in the 13th century.[ citation needed ]
The singing of carols initially suffered a decline in popularity after the Protestant Reformation in northern Europe, although some Reformers, like Martin Luther, wrote carols and encouraged their use in worship. Carols largely survived in rural communities until the revival of interest in popular songs in the 19th century. The 18th-century English reformer Charles Wesley understood the importance of music to worship. In addition to setting many psalms to melodies, which were influential in the Great Awakening in the United States, he wrote texts for at least three Christmas carols. The best known was originally entitled "Hark! How All the Welkin Rings", later renamed "Hark! the Herald Angels Sing".[188]
Completely secular Christmas seasonal songs emerged in the late 18th century. "Deck the Halls" dates from 1784, and the American "Jingle Bells" was copyrighted in 1857. In the 19th and 20th centuries, African American spirituals and songs about Christmas, based in their tradition of spirituals, became more widely known. An increasing number of seasonal holiday songs were commercially produced in the 20th century, including jazz and blues variations. In addition, there was a revival of interest in early music, from groups singing folk music, such as The Revels, to performers of early medieval and classical music. John Rutter has composed many carols including "All Bells in Paradise", "Angels' Carol", "Candlelight Carol", "Donkey Carol", "Jesus Child", "Shepherd's Pipe Carol" and "Star Carol".[ citation needed ]
During the 19th Century in the United States, there was a significant adoption of Christmas traditions from German and other immgrants, as well as novels by of Charles Dickens, including The Pickwick Papers and A Christmas Carol.[189] The practices included having Christmas parties, caroling door-to-door, sending Christmas cards, giving gifts, and decorating houses and trees. People displayed nativity scenes and crèches.[189] There were several American Christmas carols composed during the 19th Century, including "It Came Upon the Midnight Clear" in 1849, "I Heard the Bells on Christmas Day" in 1863, and "Away in a Manger" in 1885.[189] This time period marked the start of the present-day tradition of American and British choral groups performing Handel's Messiah during Christmas, rather than during Easter.[189]
The Christmas music in the U.S. was influenced by community and church music, as well as radio, television, and recordings.[189] Radio has covered Christmas music from variety shows from the 1940s and 1950s, as well as modern-day stations that exclusively play Christmas music from late November through December 25.[189] Hollywood movies have featured new Christmas music, such as "White Christmas" in Holiday Inn and Rudolph the Red-Nosed Reindeer.[189] Traditional carols have also been included in Hollywood films, such as "Hark the Herald Angels Sing" in It's a Wonderful Life (1946), and "Silent Night" in A Christmas Story.[189] American Christmas songs include religious carols and hymns, as well as secular songs featuring goodwill, Santa Claus, and gift-giving.[189]
Traditional cuisine


A special Christmas family meal is traditionally an important part of the holiday's celebration, and the food that is served varies greatly from country to country. Some regions have special meals for Christmas Eve, such as Sicily, where 12 kinds of fish are served. In the United Kingdom and countries influenced by its traditions, a standard Christmas meal includes turkey, goose or other large bird, gravy, potatoes, vegetables, sometimes bread and cider. Special desserts are also prepared, such as Christmas pudding, mince pies, Christmas cake, Panettone and Yule log cake.[190] [191] Traditional Christmas meal in Central Europe is fried carp or other fish.[192]
Cards

A 1907 Christmas card with Santa and some of his reindeer
Christmas cards are illustrated messages of greeting exchanged between friends and family members during the weeks preceding Christmas Day. The traditional greeting reads "wishing you a Merry Christmas and a Happy New Year", much like that of the first commercial Christmas card, produced by Sir Henry Cole in London in 1843.[193] The custom of sending them has become popular among a wide cross-section of people with the emergence of the modern trend towards exchanging E-cards.[194] [195]
Christmas cards are purchased in considerable quantities and feature artwork, commercially designed and relevant to the season. The content of the design might relate directly to the Christmas narrative, with depictions of the Nativity of Jesus, or Christian symbols such as the Star of Bethlehem, or a white dove, which can represent both the Holy Spirit and Peace on Earth. Other Christmas cards are more secular and can depict Christmas traditions, mythical figures such as Santa Claus, objects directly associated with Christmas such as candles, holly, and baubles, or a variety of images associated with the season, such as Christmastide activities, snow scenes, and the wildlife of the northern winter. There are even humorous cards and genres depicting nostalgic scenes of the past such as crinolined shoppers in idealized 19th-century streetscapes.[ citation needed ]
Some prefer cards with a poem, prayer, or Biblical verse; while others distance themselves from religion with an all-inclusive "Season's greetings".[196]
Commemorative stamps
A number of nations have issued commemorative stamps at Christmastide. Postal customers will often use these stamps to mail Christmas cards, and they are popular with philatelists. These stamps are regular postage stamps, unlike Christmas seals, and are valid for postage year-round. They usually go on sale sometime between early October and early December and are printed in considerable quantities.
Gift giving

Christmas gifts under a Christmas tree
The exchanging of gifts is one of the core aspects of the modern Christmas celebration, making it the most profitable time of year for retailers and businesses throughout the world. On Christmas, people exchange gifts based on the Christian tradition associated with Saint Nicholas,[197] and the gifts of gold, frankincense, and myrrh which were given to the baby Jesus by the Magi.[198] [199] The practice of gift giving in the Roman celebration of Saturnalia may have influenced Christian customs, but on the other hand the Christian "core dogma of the Incarnation, however, solidly established the giving and receiving of gifts as the structural principle of that recurrent yet unique event", because it was the Biblical Magi, "together with all their fellow men, who received the gift of God through man's renewed participation in the divine life."[200]
Gift-bearing figures
A number of figures are associated with Christmas and the seasonal giving of gifts. Among these are Father Christmas, also known as Santa Claus (derived from the Dutch for Saint Nicholas), Père Noël, and the Weihnachtsmann; Saint Nicholas or Sinterklaas; the Christkind; Kris Kringle; Joulupukki; tomte/nisse; Babbo Natale; Saint Basil; and Ded Moroz. The Scandinavian tomte (also called nisse) is sometimes depicted as a gnome instead of Santa Claus.

The best known of these figures today is red-dressed Santa Claus, of diverse origins. The name Santa Claus can be traced back to the Dutch Sinterklaas, which means simply Saint Nicholas. Nicholas was a 4th-century Greek bishop of Myra, a city in the Roman province of Lycia, whose ruins are 3 kilometres (1.9 mi) from modern Demre in southwest Turkey.[202] [203] Among other saintly attributes, he was noted for the care of children, generosity, and the giving of gifts. His feast day, December 6, came to be celebrated in many countries with the giving of gifts.[100]
Saint Nicholas traditionally appeared in bishop's attire, accompanied by helpers, inquiring about the behaviour of children during the past year before deciding whether they deserved a gift or not. By the 13th century, Saint Nicholas was well known in the Netherlands, and the practice of gift-giving in his name spread to other parts of central and southern Europe. At the Reformation in 16th–17th-century Europe, many Protestants changed the gift bringer to the Christ Child or Christkindl, corrupted in English to Kris Kringle, and the date of giving gifts changed from December 6 to Christmas Eve.[100]
The modern popular image of Santa Claus, however, was created in the United States, and in particular in New York. The transformation was accomplished with the aid of notable contributors including Washington Irving and the German-American cartoonist Thomas Nast (1840–1902). Following the American Revolutionary War, some of the inhabitants of New York City sought out symbols of the city's non-English past. New York had originally been established as the Dutch colonial town of New Amsterdam and the Dutch Sinterklaas tradition was reinvented as Saint Nicholas.[204]
Current tradition in several Latin American countries (such as Venezuela and Colombia) holds that while Santa makes the toys, he then gives them to the Baby Jesus, who is the one who actually delivers them to the children's homes, a reconciliation between traditional religious beliefs and the iconography of Santa Claus imported from the United States.
In South Tyrol (Italy), Austria, Czech Republic, Southern Germany, Hungary, Liechtenstein, Slovakia, and Switzerland, the Christkind (Ježíšek in Czech, Jézuska in Hungarian and Ježiško in Slovak) brings the presents. Greek children get their presents from Saint Basil on New Year's Eve, the eve of that saint's liturgical feast.[205] The German St. Nikolaus is not identical with the Weihnachtsmann (who is the German version of Santa Claus / Father Christmas). St. Nikolaus wears a bishop's dress and still brings small gifts (usually candies, nuts, and fruits) on December 6 and is accompanied by Knecht Ruprecht. Although many parents around the world routinely teach their children about Santa Claus and other gift bringers, some have come to reject this practice, considering it deceptive.[206]
Multiple gift-giver figures exist in Poland, varying between regions and individual families. St Nicholas (Święty Mikołaj) dominates Central and North-East areas, the Starman (Gwiazdor) is most common in Greater Poland, Baby Jesus (Dzieciątko) is unique to Upper Silesia, with the Little Star (Gwiazdka) and the Little Angel (Aniołek) being common in the South and the South-East. Grandfather Frost (Dziadek Mróz) is less commonly accepted in some areas of Eastern Poland.[207] [208] It is worth noting that across all of Poland, St Nicholas is the gift giver on the Saint Nicholas Day on December 6.
Date according to Julian calendar
Some jurisdictions of the Eastern Orthodox Church, including those of Russia, Georgia, Ukraine, Macedonia, Montenegro, Serbia, and Jerusalem, mark feasts using the older Julian calendar. As of 2021, there is a difference of 13 days between the Julian calendar and the modern Gregorian calendar, which is used internationally for most secular purposes. As a result, December 25 on the Julian calendar currently corresponds to January 7 on the calendar used by most governments and people in everyday life. Therefore, the aforementioned Orthodox Christians mark December 25 (and thus Christmas) on the day that is internationally considered to be January 7.[5]
However, other Orthodox Christians, such as those belonging to the jurisdictions of Constantinople, Bulgaria, Greece, Romania, Antioch, Alexandria, Albania, Cyprus, Finland, and the Orthodox Church in America, among others, began using the Revised Julian calendar in the early 20th century, which at present corresponds exactly to the Gregorian calendar.[209] Therefore, these Orthodox Christians mark December 25 (and thus Christmas) on the same day that is internationally considered to be December 25, and which is also the date of Christmas among Western Christians.[ citation needed ]
A further complication is added by the fact that the Armenian Apostolic Church continues the original ancient Eastern Christian practice of celebrating the birth of Christ not as a separate holiday, but on the same day as the celebration of his baptism (Theophany), which is on January 6. This is a public holiday in Armenia, and it is held on the same day that is internationally considered to be January 6, because the Armenian Church in Armenia uses the Gregorian calendar.[ citation needed ]
However, there is also a small Armenian Patriarchate of Jerusalem, which maintains the traditional Armenian custom of celebrating the birth of Christ on the same day as Theophany (January 6), but uses the Julian calendar for the determination of that date. As a result, this church celebrates "Christmas" (more properly called Theophany) on the day that is considered January 19 on the Gregorian calendar in use by the majority of the world.[ citation needed ]
In summary, there are four different dates used by different Christian groups to mark the birth of Christ, given in the table below.
Listing
| Church or section | Date | Calendar | Gregorian date | Note |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Armenian Patriarchate of Jerusalem | January 6 | Julian calendar | January 19 | Correspondence between Julian January 6 and Gregorian January 19 holds until 2100; in the following century the difference will be one day more.[ citation needed ] |
| Armenian Apostolic Church, Armenian Catholic Church, Armenian Evangelical Church | January 6 | Gregorian calendar | January 6 | |
| Some Anabaptists, such as the Amish[8] | December 25 | Julian calendar | January 6 | Old Christmas |
| Eastern Orthodox Church jurisdictions, including those of Constantinople, Bulgaria, Greece, Romania, Antioch, Alexandria, Albania, Cyprus, Finland, and the Orthodox Church in America | December 25 | Revised Julian calendar | December 25 | Revised Julian calendar usage started in the early 20th century[ citation needed ] |
| Other Eastern Orthodox: Russia, Georgia, Ukraine, Macedonia, Belarus, Moldova, Montenegro, Serbia and Jerusalem. Also, some Byzantine Rite Catholics and Byzantine Rite Lutherans. | December 25 | Julian calendar | January 7 | Correspondence between Julian December 25 and Gregorian January 7 of the following year holds until 2100; from 2101 to 2199 the difference will be one day more.[ citation needed ] |
| Coptic Orthodox Church | Koiak 29 or 28 (corresponding to Julian December 25) | Coptic calendar | January 7 | After the Coptic insertion of a leap day in what for the Julian calendar is August (September in Gregorian), Christmas is celebrated on Koiak 28 in order to maintain the exact interval of nine 30-day months and 5 days of the child's gestation.[ citation needed ] |
| Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church (sole date), Eritrean Orthodox Tewahedo Church (sole date), and P'ent'ay (Ethiopian-Eritrean Evangelical) Churches (primary date) | Tahsas 29 or 28 (corresponding to Julian December 25) | Ethiopian Calendar | January 7 | After the Ethiopian and Eritrean insertion of a leap day in what for the Julian calendar is August (September in Gregorian), Christmas is celebrated on Tahsas 28 in order to maintain the exact interval of nine 30-day months and 5 days of the child's gestation.[210] Most Protestants (P'ent'ay/Evangelicals) in the diaspora have the option of choosing the Ethiopian calendar (Tahsas 29/January 7) or the Gregorian calendar (December 25) for religious holidays, with this option being used when the corresponding eastern celebration is not a public holiday in the western world (with most diaspora Protestants celebrating both days).[ citation needed ] |
| Most Western Christian Churches, most Eastern Catholic churches and civil calendars | December 25 | Gregorian calendar | December 25 |
Economy

Christmas decorations at the Galeries Lafayette department store in Paris, France. The Christmas season is the busiest trading period for retailers.

Christmas market in Jena, Germany
Christmas is typically a peak selling season for retailers in many nations around the world. Sales increase dramatically as people purchase gifts, decorations, and supplies to celebrate. In the United States, the "Christmas shopping season" starts as early as October.[211] [212] In Canada, merchants begin advertising campaigns just before Halloween (October 31), and step up their marketing following Remembrance Day on November 11. In the UK and Ireland, the Christmas shopping season starts from mid-November, around the time when high street Christmas lights are turned on.[213] [214] In the United States, it has been calculated that a quarter of all personal spending takes place during the Christmas/holiday shopping season.[215] Figures from the U.S. Census Bureau reveal that expenditure in department stores nationwide rose from $20.8 billion in November 2004 to $31.9 billion in December 2004, an increase of 54 percent. In other sectors, the pre-Christmas increase in spending was even greater, there being a November–December buying surge of 100 percent in bookstores and 170 percent in jewelry stores. In the same year employment in American retail stores rose from 1.6 million to 1.8 million in the two months leading up to Christmas.[216] Industries completely dependent on Christmas include Christmas cards, of which 1.9 billion are sent in the United States each year, and live Christmas Trees, of which 20.8 million were cut in the U.S. in 2002.[217] For 2019, the average US adult was projected to spend $920 on gifts alone.[218] In the UK in 2010, up to £8 billion was expected to be spent online at Christmas, approximately a quarter of total retail festive sales.[214]

In most Western nations, Christmas Day is the least active day of the year for business and commerce; almost all retail, commercial and institutional businesses are closed, and almost all industries cease activity (more than any other day of the year), whether laws require such or not. In England and Wales, the Christmas Day (Trading) Act 2004 prevents all large shops from trading on Christmas Day. Similar legislation was approved in Scotland with the Christmas Day and New Year's Day Trading (Scotland) Act 2007. Film studios release many high-budget movies during the holiday season, including Christmas films, fantasy movies or high-tone dramas with high production values to hopes of maximizing the chance of nominations for the Academy Awards.[219]
One economist's analysis calculates that, despite increased overall spending, Christmas is a deadweight loss under orthodox microeconomic theory, because of the effect of gift-giving. This loss is calculated as the difference between what the gift giver spent on the item and what the gift receiver would have paid for the item. It is estimated that in 2001, Christmas resulted in a $4 billion deadweight loss in the U.S. alone.[220] [221] Because of complicating factors, this analysis is sometimes used to discuss possible flaws in current microeconomic theory. Other deadweight losses include the effects of Christmas on the environment and the fact that material gifts are often perceived as white elephants, imposing cost for upkeep and storage and contributing to clutter.[222]
Controversies

Christmas has at times been the subject of controversy and attacks from various sources. Historically it was prohibited by Puritans when they briefly held power in England (1647–1660), and in Colonial America where the Puritans outlawed the celebration of Christmas in 1659.[224] [225] The Parliament of Scotland, which was dominated by Presbyterians, passed a series of acts outlawing the observance of Christmas between 1637 and 1690; Christmas Day did not become a public holiday in Scotland until 1958.[226] Christmas celebrations have also been prohibited by atheist states such as the Soviet Union[227] and more recently majority Muslim states such as Somalia, Tajikistan and Brunei.[228]
Some Christians and organizations such as Pat Robertson's American Center for Law and Justice cite alleged attacks on Christmas (dubbing them a "war on Christmas").[229] Such groups claim that any specific mention of the term "Christmas" or its religious aspects is being increasingly censored, avoided, or discouraged by a number of advertisers, retailers, government (prominently schools), and other public and private organizations. One controversy is the occurrence of Christmas trees being renamed Holiday trees.[230] In the U.S. there has been a tendency to replace the greeting Merry Christmas with Happy Holidays, which is considered inclusive at the time of the Jewish celebration of Hanukkah,[231] Kwanzaa, and Humanlight. In the U.S. and Canada, where the use of the term "Holidays" is most prevalent, opponents have denounced its usage and avoidance of using the term "Christmas" as being politically correct.[232] [233] [234] In 1984, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in Lynch v. Donnelly that a Christmas display (which included a Nativity scene) owned and displayed by the city of Pawtucket, Rhode Island, did not violate the First Amendment.[235] American Muslim scholar Abdul Malik Mujahid has said that Muslims must treat Christmas with respect, even if they disagree with it.[236]
The government of the People's Republic of China officially espouses state atheism,[237] and has conducted antireligious campaigns to this end.[238] In December 2018, officials raided Christian churches just prior to Christmastide and coerced them to close; Christmas trees and Santa Clauses were also forcibly removed.[239] [240]
See also
- Christmas in July – Second Christmas celebration
- Christmas Peace – Finnish tradition
- Christmas Sunday – Sunday after Christmas
- List of Christmas novels – Wikipedia list article
- Little Christmas – Alternative title for 6 January
- Nochebuena – Spanish term for Christmas Eve
- Mawlid – Birthday of Muhammad
- Twin Holy Birthdays – Baháʼí religious observance
- Yaldā Night – Persian festival
- Christmas by medium – Christmas represented in different media
Notes
- ^ Several branches of Eastern Christianity that use the Julian calendar also celebrate on December 25 according to that calendar, which is now January 7 on the Gregorian calendar. Armenian Churches observed the nativity on January 6 even before the Gregorian calendar originated. Most Armenian Christians use the Gregorian calendar, still celebrating Christmas Day on January 6. Some Armenian churches use the Julian calendar, thus celebrating Christmas Day on January 19 on the Gregorian calendar, with January 18 being Christmas Eve. Some regions also celebrate primarily on December 24, rather than December 25.
References
- ^ a b "Christmas as a Multi-Faith Festival" (PDF). BBC Learning English. December 29, 2005. Archived (PDF) from the original on October 1, 2008. Retrieved September 30, 2008.
- ^ a b "In the U.S., Christmas Not Just for Christians". Gallup, Inc. December 24, 2008. Archived from the original on November 16, 2012. Retrieved December 16, 2012.
- ^ a b c d e f Martindale, Cyril Charles (1908). "Christmas". The Catholic Encyclopedia. 3. New York: Robert Appleton Company.
- ^ Gwynne, Paul (2011). World Religions in Practice. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN978-1-4443-6005-9.
- ^ a b Ramzy, John. "The Glorious Feast of Nativity: 7 January? 29 Kiahk? 25 December?". Coptic Orthodox Church Network. Archived from the original on December 28, 2010. Retrieved January 17, 2011.
- ^ Steinfels, Peter (January 6, 2007). "At Armenian Churches, a Distinct Observance Today". The New York Times. Archived from the original on June 12, 2018. Retrieved June 12, 2018.
- ^ Agadjanian, Alexander (2016). Armenian Christianity Today: Identity Politics and Popular Practice. Routledge. p. 113. ISBN9781317178576.
The Armenian Apostolic Church follows the oldest Jerusalem version of Canons of Calendar, based on the Julian Calendar, and therefore celebrates Christmas and Theophany on the same day, January 6
- ^ a b "Why do Amish celebrate "Old" Christmas?". Dutchman News. December 17, 2009. Archived from the original on December 26, 2018. Retrieved January 12, 2019.
- ^ Jansezian, Nicole. "10 things to do over Christmas in the Holy Land". The Jerusalem Post. Archived from the original on December 26, 2014. Retrieved December 26, 2014.
the Armenians in Jerusalem – and only in Jerusalem – celebrate Christmas on January 19...
- ^ "The Global Religious Landscape | Christians". Pew Research Center. December 18, 2012. Archived from the original on March 10, 2015. Retrieved May 23, 2014.
- ^ "Christmas Strongly Religious For Half in U.S. Who Celebrate It". Gallup, Inc. December 24, 2010. Archived from the original on December 7, 2012. Retrieved December 16, 2012.
- ^ Forbes, Bruce David (October 1, 2008). Christmas: A Candid History. University of California Press. p. 27. ISBN978-0-520-25802-0.
In 567 the Council of Tours proclaimed that the entire period between Christmas and Epiphany should be considered part of the celebration, creating what became known as the twelve days of Christmas, or what the English called Christmastide.
On the last of the twelve days, called Twelfth Night, various cultures developed a wide range of additional special festivities. The variation extends even to the issue of how to count the days. If Christmas Day is the first of the twelve days, then Twelfth Night would be on January 5, the eve of Epiphany. If December 26, the day after Christmas, is the first day, then Twelfth Night falls on January 6, the evening of Epiphany itself.
After Christmas and Epiphany were in place, on December 25 and January 6, with the twelve days of Christmas in between, Christians slowly adopted a period called Advent, as a time of spiritual preparation leading up to Christmas. - ^ Canadian Heritage – Public holidaysArchived November 24, 2009, at the Wayback Machine – Government of Canada. Retrieved November 27, 2009.
- ^ 2009 Federal Holidays Archived January 16, 2013, at the Wayback Machine – U.S. Office of Personnel Management. Retrieved November 27, 2009.
- ^ Bank holidays and British Summer time Archived May 15, 2011, at the Wayback Machine – HM Government. Retrieved November 27, 2009.
- ^ Ehorn, Lee Ellen; Hewlett, Shirely J.; Hewlett, Dale M. (September 1, 1995). December Holiday Customs. Lorenz Educational Press. p. 1. ISBN978-1-4291-0896-6.
- ^ Nick Hytrek, "Non-Christians focus on secular side of Christmas" Archived November 14, 2009, at the Wayback Machine, Sioux City Journal, November 10, 2009. Retrieved November 18, 2009.
- ^ Crump, William D. (September 15, 2001). The Christmas Encyclopedia (3 ed.). McFarland. p. 39. ISBN9780786468270.
Christians believe that a number of passages in the Bible are prophecies about future events in the life of the promised Messiah or Jesus Christ. Most, but not all, of those prophecies are found in the Old Testament ... Born in Bethlehem (Micah 5:2): "But thou, Bethlehem Ephratah, though thou be little among the thousands of Juda, yet out of thee shall he come forth unto me that is to be ruler in Israel; whose goings forth have been from of old, from everlasting."
- ^ Tucker, Ruth A. (2011). Parade of Faith: A Biographical History of the Christian Church. Zondervan. p. 23. ISBN9780310206385.
According to gospel accounts, Jesus was born during the reign of Herod the Great, thus sometime before 4 BCE. The birth narrative in Luke's gospel is one of the most familiar passages in the Bible. Leaving their hometown of Nazareth, Mary and Joseph travel to Bethlehem to pay taxes. Arriving late, they find no vacancy at the inn. They are, however, offered a stable, most likely a second room attached to a family dwelling where animals were sheltered—a room that would offer some privacy from the main family room for cooking, eating, and sleeping. This "city of David" is the little town of Bethlehem of Christmas-carol fame, a starlit silhouette indelibly etched on Christmas cards. No sooner was the baby born than angels announced the news to shepherds who spread the word.
- ^ Corinna Laughlin, Michael R. Prendergast, Robert C. Rabe, Corinna Laughlin, Jill Maria Murdy, Therese Brown, Mary Patricia Storms, Ann E. Degenhard, Jill Maria Murdy, Ann E. Degenhard, Therese Brown, Robert C. Rabe, Mary Patricia Storms, Michael R. Prendergast, Sourcebook for Sundays, Seasons, and Weekdays 2011: The Almanac for Pastoral Liturgy Archived April 7, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, LiturgyTrainingPublications, 2010, p. 29.
- ^ "The Chronography of 354 AD. Part 12: Commemorations of the Martyrs" Archived November 22, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, The Tertullian Project. 2006. Retrieved November 24, 2011.
- ^ Roll, Susan K. (1995). Toward the Origins of Christmas. Peeters Publishers. p. 133. ISBN9789039005316.
- ^ a b c Bradt, Hale, Astronomy Methods, (2004), p. 69.
Roll, p. 87. - ^ The Liturgical Year. Thomas Nelson. November 3, 2009. ISBN978-1-4185-8073-5 . Retrieved April 2, 2009.
Christmas is not really about the celebration of a birth date at all. It is about the celebration of a birth. The fact of the date and the fact of the birth are two different things. The calendrical verification of the feast itself is not really that important ... What is important to the understanding of a life-changing moment is that it happened, not necessarily where or when it happened. The message is clear: Christmas is not about marking the actual birth date of Jesus. It is about the Incarnation of the One who became like us in all things but sin (Hebrews 4:15) and who humbled Himself "to the point of death-even death on a cross" (Phil. 2:8). Christmas is a pinnacle feast, yes, but it is not the beginning of the liturgical year. It is a memorial, a remembrance, of the birth of Jesus, not really a celebration of the day itself. We remember that because the Jesus of history was born, the Resurrection of the Christ of faith could happen.
- ^ "The Christmas Season". CRI / Voice, Institute. Archived from the original on April 7, 2009. Retrieved April 2, 2009.
The origins of the celebrations of Christmas and Epiphany, as well as the dates on which they are observed, are rooted deeply in the history of the early church. There has been much scholarly debate concerning the exact time of the year when Jesus was born, and even in what year he was born. Actually, we do not know either. The best estimate is that Jesus was probably born in the springtime, somewhere between the years of 6 and 4 BC, as December is in the middle of the cold rainy season in Bethlehem, when the sheep are kept inside and not on pasture as told in the Bible. The lack of a consistent system of timekeeping in the first century, mistakes in later calendars and calculations, and lack of historical details to cross-reference events have led to this imprecision in fixing Jesus' birth. This suggests that the Christmas celebration is not an observance of a historical date, but a commemoration of the event in terms of worship.
- ^ The School Journal, Volume 49. Harvard University. 1894. Retrieved April 2, 2009.
Throughout the Christian world the 25th of December is celebrated as the birthday of Jesus Christ. There was a time when the churches were not united regarding the date of the joyous event. Many Christians kept their Christmas in April, others in May, and still others at the close of September, till finally December 25 was agreed upon as the most appropriate date. The choice of that day was, of course, wholly arbitrary, for neither the exact date not the period of the year at which the birth of Christ occurred is known. For purposes of commemoration, however, it is unimportant whether the celebration shall fall or not at the precise anniversary of the joyous event.
- ^ West's Federal Supplement. West Publishing Company. 1990.
While the Washington and King birthdays are exclusively secular holidays, Christmas has both secular and religious aspects.
- ^ "Poll: In a changing nation, Santa endures". Associated Press. December 22, 2006. Archived from the original on December 26, 2018. Retrieved December 24, 2018.
- ^ Schoenborn, Christoph (1994). God's human face: the Christ-icon. p. 154. ISBN978-0-89870-514-0.
- ^ Galey, John (1986). Sinai and the Monastery of St. Catherine. p. 92. ISBN978-977-424-118-5.
- ^ Christenmas, n., Oxford English Dictionary. Retrieved December 12.
- ^ a b "Christmas" in the Middle English Dictionary. Archived January 5, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Griffiths, Emma (December 22, 2004). "Why get cross about Xmas?". BBC News. Archived from the original on November 11, 2011. Retrieved December 12, 2011.
- ^ a b Hutton, Ronald (2001). The Stations of the Sun: A History of the Ritual Year in Britain. Oxford University Press. ISBN9780192854483.
- ^ "Midwinter" in Bosworth & Toller. Archived January 13, 2012, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Serjeantson, Mary Sidney (1968). A History of Foreign Words in English.
- ^ "Online Etymology Dictionary". Archived from the original on January 13, 2012. Retrieved December 13, 2011.
- ^ Yule Archived January 13, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved December 12.
- ^ Noel Archived January 13, 2012, at the Wayback Machine Online Etymology Dictionary. Retrieved December 12.
- ^ "Biblical literature" Archived April 26, 2015, at the Wayback Machine, Encyclopædia Britannica, 2011. Web. January 22, 2011.
- ^ "Matthew Chapter 2". Enduring Word. December 8, 2015. Retrieved December 25, 2020.
- ^ a b Hijmans, S.E., Sol: The Sun in the Art and Religions of Rome, 2009, p. 584.
- ^ a b Malachi 4:2.
- ^ "Christmas and its cycle". New Catholic Encyclopedia. 3 (2nd ed.). Catholic University of America Press. 2002. pp. 550–557.
- ^ "The Chronography of 354 AD. Part 12: Commemorations of the Martyrs. Archived February 21, 2017, at the Wayback Machine." MGH Chronica Minora I (1892), pp.71–72. See the first entry.
- ^ McGowan, Andrew, How December 25 Became Christmas Archived December 14, 2012, at the Wayback Machine, Bible History Daily, February 12, 2016.
- ^ Melton, J. Gordon (2011). Religious Celebrations: An Encyclopedia of Holidays, Festivals, Solemn Observances, and Spiritual Commemorations [2 volumes]: An Encyclopedia of Holidays, Festivals, Solemn Observances, and Spiritual Commemorations. ABC-CLIO. p. 39. ISBN978-1-59884-206-7.
The March 25 date, which tied together the beginning of Mary's pregnancy and the incarnation of God in Jesus as occurring nine months before Christmas (December 25), supplied the rationale for setting the beginning of the ecclesiastical and legal year. ... Both the Anglicans and the Lutherans have continued to observe the March 25 date for celebrating the Annunciation.
- ^ a b c d e f Durston, Chris (December 1985). "Lords of Misrule: The Puritan War on Christmas 1642–60". History Today. Vol. 35 no. 12. pp. 7–14. Archived from the original on March 10, 2007.
- ^ a b c Rowell, Geoffrey (December 1993). "Dickens and the Construction of Christmas". History Today. 43 (12). Archived from the original on December 29, 2016. Retrieved December 28, 2016.
There is no doubt that A Christmas Carol is first and foremost a story concerned with the Christian gospel of liberation by the grace of God, and with incarnational religion which refuses to drive a wedge between the world of spirit and the world of matter. Both the Christmas dinners and the Christmas dinner-carriers are blessed; the cornucopia of Christmas food and feasting reflects both the goodness of creation and the joy of heaven. It is a significant sign of a shift in theological emphasis in the nineteenth century from a stress on the Atonement to a stress on the Incarnation, a stress which found outward and visible form in the sacramentalism of the Oxford Movement, the development of richer and more symbolic forms of worship, the building of neo-Gothic churches, and the revival and increasing centrality of the keeping of Christmas itself as a Christian festival. ... In the course of the century, under the influence of the Oxford Movement's concern for the better observance of Christian festivals, Christmas became more and more prominent. By the later part of the century cathedrals provided special services and musical events, and might have revived ancient special charities for the poor – though we must not forget the problems for large: parish-church cathedrals like Manchester, which on one Christmas Day had no less than eighty couples coming to be married (the signing of the registers lasted until four in the afternoon). The popularity of Dickens' A Christmas Carol played a significant part in the changing consciousness of Christmas and the way in which it was celebrated. The popularity of his public readings of the story is an indication of how much it resonated with the contemporary mood, and contributed to the increasing place of the Christmas celebration in both secular and religious ways that was firmly established by the end of the nineteenth century.
- ^ a b Rowell, Geoffrey, "Dickens and the Construction of Christmas", History Today, Volume: 43 Issue: 12, December 1993, pp. 17–24.
- ^ Ledger, Sally; Furneaux, Holly, eds. (2011). Charles Dickens in Context. Cambridge University Press. p. 178. ISBN978-0-19-513886-3 . Retrieved December 25, 2020.
- ^ McCracken, George, Arnobius of Sicca, the Case Against the Pagans, Volume 2, p. 83. "Therefore if this is a fact, how can Jupiter be god if it is agreed that god is everlasting, while the other is represented by you to have a birthday, and frightened by the new experience, to have squalled like an infant."
- ^ The manuscript reads, VIII kal. Ian. natus Christus in Betleem Iudeae. ("The Chronography of 354 AD. Part 12: Commemorations of the Martyrs Archived November 22, 2011, at the Wayback Machine," The Tertullian Project. 2006.)
- ^ Wainwright, Geoffrey; Westerfield Tucker, Karen Beth, eds. (2005). The Oxford History of Christian Worship. Oxford University Press. p. 65. ISBN978-0-19-513886-3 . Retrieved February 3, 2012.
- ^ a b Roy, Christian (2005). Traditional Festivals: A Multicultural Encyclopedia. Santa Barbara, California: ABC-CLIO. p. 146. ISBN978-1-57607-089-5. Archived from the original on January 11, 2014. Retrieved February 3, 2012.
- ^ Pokhilko, Hieromonk Nicholas. "History of Epiphany". Archived from the original on September 23, 2016. Retrieved December 27, 2017.
- ^ Hastings, James; Selbie, John A., eds. (2003). Encyclopedia of Religion and Ethics. 6. Kessinger Publishing Company. pp. 603–604. ISBN978-0-7661-3676-2. Archived from the original on November 22, 2018. Retrieved February 3, 2012.
- ^ Kelly, Joseph F., The Origins of Christmas, Liturgical Press, 2004, pp. 67–69.
- ^ "Bruma Archived October 10, 2006, at the Wayback Machine", Seasonal Festivals of the Greeks and Romans
Pliny the Elder, Natural History, 18:59 - ^ Augustine, Sermon 192 Archived November 25, 2016, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Roll, Susan K. (1995). Towards the Origin of Christmas. Kok Pharos Publishing. p. 82, cf. note 115. ISBN978-90-390-0531-6. Archived from the original on December 31, 2015. Retrieved December 25, 2013.
- ^ Newton, Isaac, Observations on the Prophecies of Daniel, and the Apocalypse of St. John Archived September 18, 2012, at the Wayback Machine (1733). Ch. XI. A sun connection is possible because Christians considered Jesus to be the "Sun of righteousness" prophesied in Malachi 4:2: "But for you who fear my name, the sun of righteousness shall rise with healing in its wings. You shall go out leaping like calves from the stall."
- ^ a b Hijmans, S.E., Sol, the sun in the art and religions of Rome, 2009, p. 595. ISBN 978-90-367-3931-3 Archived May 10, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b Bradshaw, Paul F., "Christmas" Archived January 9, 2017, at the Wayback Machine, The New SCM Dictionary of Liturgy of Worship, Hymns Ancient and Modern Ltd., 2002.
- ^ Roll, pp. 88–90.
Duchesne, Louis, Les Origines du Culte Chrétien, Paris, 1902, 262 ff. - ^ Andrew McGowan. "How December 25 Became Christmas". Bible Review & Bible History Daily. Biblical Archaeology Society. Archived from the original on December 14, 2012. Retrieved February 24, 2011.
- ^ "Annunciation", New Catholic Encyclopedia 2nd edition, 2003, Catholic University of America Press.
- ^ 1 Corinthians 5:7–8: "Our paschal lamb, Christ, has been sacrificed. Therefore let us celebrate the festival..."
Tally, pp. 2–4. - ^ Roll, p. 87.
- ^ Roll (1995), p. 88
- ^ Collinge, William J. (2012). Historical Dictionary of Catholicism. ISBN9780810857551. Archived from the original on December 31, 2015. Retrieved December 23, 2014.
- ^ Hippolytus and December 25th as the date of Jesus' birth Archived September 13, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, Roll (1995), p. 87.
- ^ Kelly, Joseph F. (2004). The Origins of Christmas. Liturgical Press. p. 60. ISBN978-0-8146-2984-0. Online here [1] Archived February 19, 2017, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Pearse, Roger (December 26, 2019). "Some notes on "De solstitiis et aequinoctis" (CPL 2277)". Roger Pearse . Retrieved April 9, 2021.
- ^ Roll, Susan K. (1995). Towards the Origin of Christmas. Kok Pharos Publishing. p. 97, cf. note 173. ISBN978-90-390-0531-6. Archived from the original on April 9, 2021. Retrieved April 9, 2021.
- ^ a b Oxford Dictionary of the Christian Church (Oxford University Press, 2005, ISBN 978-0-19-280290-3), article "Christmas".
- ^ Senn, Frank C. (2012). Introduction to Christian Liturgy. ISBN9781451424331. Archived from the original on December 31, 2015. Retrieved December 23, 2014.
- ^ (cited in Christianity and Paganism in the Fourth to Eighth Centuries, Ramsay MacMullen. Yale:1997, p. 155).
- ^ "Christmas Archived August 31, 2009, at the Wayback Machine", Encarta. 2009-10-31.
Roll, Susan K. (1995). Toward the Origins of Christmas. Peeters Publishers. p. 130. ISBN9789039005316. Archived from the original on November 2, 2015. Retrieved June 20, 2015. - ^ Tighe, William J. (2003). "Calculating Christmas". Touchstone. 16 (10). Archived from the original on December 11, 2008. Retrieved November 17, 2008.
- ^ Hermann Usener, Das Weihnachtsfest. In: Religionsgeschichtliche Untersuchungen, part 1. Second edition. Verlag von Max Cohen & Sohn, Bonn 1911. (Note that the first edition, 1889, doesn't have the discussion of Natalis Solis Invicti); also Sol Invictus (1905).
- ^ Talley, Thomas J. (1991). The Origins of the Liturgical Year. Liturgical Press. pp. 88–91. ISBN978-0-8146-6075-1 . Retrieved December 27, 2016.
- ^ "Although this view is still very common, it has been seriously challenged" – Church of England Liturgical Commission, The Promise of His Glory: Services and Prayers for the Season from All Saints to Candlemas (Church House Publishing 1991 ISBN 978-0-71513738-3) quoted in "The Date of Christmas and Epiphany" Archived April 6, 2015, at the Wayback Machine.
- ^ Hijmans, S.E. (2009). The Sun in the Art and Religions of Rome. p. 588. ISBN978-90-367-3931-3. Archived from the original on May 10, 2013.
- ^ Michael Alan Anderson, Symbols of Saints: Theology, ritual, and kinship in music for John the Baptist and St. Anne (1175–1563) The University of Chicago, UMI / ProQuest Dissertations Publishing, Ann Arbor 2008, pp. 42–46, ISBN 978-0-54956551-2.
- ^ Tucker, Karen B. Westerfield (2000). "Christmas". In Hastings, Adrian; Mason, Alistair; Pyper, Hugh (eds.). The Oxford Companion to Christian Thought. Oxford University Press. p. 114. ISBN978-0-19-860024-4.
- ^ a b c d e f g Murray, Alexander, "Medieval Christmas" Archived December 13, 2011, at the Wayback Machine, History Today, December 1986, 36 (12), pp. 31 – 39.
- ^ a b Standiford, Les (2008). The Man Who Invented Christmas: How Charles Dickens's A Christmas Carol Rescued His Career and Revived Our Holiday Spirits. Crown. ISBN978-0-307-40578-4.
- ^ a b Minzesheimer, Bob (December 22, 2008). "Dickens' classic 'Christmas Carol' still sings to us". USA Today. Archived from the original on November 6, 2009. Retrieved April 30, 2010.
- ^ Neal, Daniel (1822). The History of the Puritans. William Baynes and Son. p. 193.
They disapproved of the observation of sundry of the church-festivals or holidays, as having no foundation in Scripture, or primitive antiquity.
- ^ a b c d Barnett, James Harwood (1984). The American Christmas: A Study in National Culture. Ayer Publishing. p. 3. ISBN978-0-405-07671-8.
- ^ "Christmas – An Ancient Holiday" Archived May 9, 2007, at the Wayback Machine, The History Channel, 2007.
- ^ a b Simek (2007:379).
- ^ Coffman, Elesha. "Why December 25?" Christian History & Biography, Christianity Today, 2000.
- ^ Simek (2010:180, 379–380).
- ^ Weiser, Franz Xaver (1958). Handbook of Christian Feasts and Customs. Harcourt.
- ^ "Koliada". Encyclopediaofukraine.com. Retrieved November 19, 2012.
- ^ a b McGreevy, Patrick. "Place in the American Christmas," (JSTOR Archived December 15, 2018, at the Wayback Machine), Geographical Review, Vol. 80, No. 1. January 1990, pp. 32–42. Retrieved September 10, 2007.
- ^ a b c Restad, Penne L. (1995). Christmas in America: a History. Oxford: Oxford University Press. ISBN978-0-19-510980-1.
- ^ a b c Forbes, Bruce David, Christmas: a candid history, University of California Press, 2007, ISBN 0-520-25104-0, pp. 68–79.
- ^ Lowe, Scott C. (January 11, 2011). Christmas. John Wiley & Sons. p. 226. ISBN978-1-4443-4145-4.
- ^ Shawcross, John T. (January 1, 1993). John Milton. University Press of Kentucky. p. 249. ISBN978-0-8131-7014-5.
Milton was raised an Anglican, trained to become an Anglican minister, and remained an Anglican through the signing of the subscription books of Cambridge University in both 1629 and 1632, which demanded an allegiance to the state church and its Thirty-nine Articles.
- ^ Browne, Sammy R. A Brief Anthology of English Literature, Volume 1. p. 412. ISBN978-1-105-70569-4.
His father had wanted him to practice law but Milton considered writing poetry his life's work. At 21 years old, he wrote a poem, "On the morning of Christ's Nativity," a work that is still widely read during Christmas.
- ^ Heinz, Donald (2010). Christmas: Festival of Incarnation. Fortress Press. p. 94. ISBN978-1-4514-0695-5.
- ^ Old, Hughes Oliphant (2002). Worship: Reformed According to Scripture. Westminster John Knox Press. p. 29. ISBN978-0-664-22579-7.
Within a few years the Reformed church calendar was fairly well established. The heart of it was the weekly observance of the resurrection on the Lord's Day. Instead of liturgical seasons being observed, "the five evangelical feast days" were observed: Christmas, Good Friday, Easter, Ascension, and Pentecost. They were chosen because they were understood to mark the essential stages in the history of salvation.
- ^ Old, Hughes Oliphant (2002). Worship: Reformed According to Scripture. Westminster John Knox Press. p. 29. ISBN978-0-664-22579-7.
- ^ Carl Philipp Emanuel Nothaft (October 2011). "From Sukkot to Saturnalia: The Attack on Christmas in Sixteenth-Century Chronological Scholarship". Journal of the History of Ideas. 72 (4): 504–505. JSTOR 41337151.
However, when Thomas Mocket, rector of Gilston in Hertfordshire, decried such vices in a pamphlet to justify the parliamentary 'ban' of Christmas, effective since June 1647...
- ^ Sandys, William (1852). Christmastide: its history, festivities and carols. London: John Russell Smith. pp. 119–120.
- ^ Chambers, Robert (1885). Domestic Annals of Scotland, p. 211.
- ^ "Act dischairging the Yule vacance". The Records of the Parliaments of Scotland to 1707. (in Middle Scots). St Andrews: University of St Andrews and National Archives of Scotland. Archived from the original on May 19, 2012. Retrieved February 29, 2012.
- ^ Houston, Rab; Houston, Robert Allan (2008). Scotland: a very short introduction. Very short introductions. 197. Oxford University Press. p. 172. ISBN978-0-19-923079-2 . Retrieved February 29, 2012.
- ^ Miall, Anthony & Peter (1978). The Victorian Christmas Book. Dent. p. 7. ISBN978-0-460-12039-5.
- ^ Woodforde, James (1978). The Diary of a Country Parson 1758–1802. Oxford University Press. ISBN978-0-19-281241-4.
- ^ Innes, Stephen (1995). Creating the Commonwealth: The Economic Culture of Puritan New England. W.W. Norton & Company. p. 145. ISBN978-0-393-03584-1.
- ^ Marling, Karal Ann (2000). Merry Christmas!: Celebrating America's Greatest Holiday. Harvard University Press. p. 44. ISBN978-0-674-00318-7.
- ^ Smith Thomas, Nancy (2007). Moravian Christmas in the South. p. 20. ISBN978-0-8078-3181-6.
- ^ Andrews, Peter (1975). Christmas in Colonial and Early America. United States: World Book Encyclopedia, Inc. ISBN978-0-7166-2001-3.
- ^ Christmas in France. World Book Encyclopedia. 1996. p. 35. ISBN978-0-7166-0876-9.
Carols were altered by substituting names of prominent political leaders for royal characters in the lyrics, such as the Three Kings. Church bells were melted down for their bronze to increase the national treasury, and religious services were banned on Christmas Day. The cake of kings, too, came under attack as a symbol of royalty. It survived, however, for a while with a new name—the cake of equality.
- ^ Mason, Julia (December 21, 2015). "Why Was Christmas Renamed 'Dog Day' During the French Revolution?". HistoryBuff. Archived from the original on November 1, 2016. Retrieved November 18, 2016.
How did people celebrate the Christmas during the French Revolution? In white-knuckled terror behind closed doors. Anti-clericalism reached its apex on 10 November 1793, when a Fête de la Raison was held in honor of the Cult of Reason. Churches across France were renamed "Temples of Reason" and the Notre Dame was "de-baptized" for the occasion. The Commune spared no expense: "The first festival of reason, which took place in Notre Dame, featured a fabricated mountain, with a temple of philosophy at its summit and a script borrowed from an opera libretto. At the sound of Marie-Joseph Chénier's Hymne à la Liberté, two rows of young women, dressed in white, descended the mountain, crossing each other before the 'altar of reason' before ascending once more to greet the goddess of Liberty." As you can probably gather from the above description, 1793 was not a great time to celebrate Christmas in the capital.
- ^ Anon (May 22, 2007). "Bank Holiday Fact File" (PDF). TUC press release. TUC. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 3, 2013. Retrieved January 12, 2010.
- ^ Hutton, Ronald (February 15, 2001). The Stations of the Sun: A History of the Ritual Year in Britain. Oxford University Press. ISBN978-0-19-157842-7.
- ^ Forbes, Bruce David (October 1, 2008). Christmas: A Candid History. --University of California Press. p. 62. ISBN978-0-520-25802-0.
What Dickens did advocate in his story was "the spirit of Christmas". Sociologist James Barnett has described it as Dickens's "Carol Philosophy", which "combined religious and secular attitudes toward to celebration into a humanitarian pattern. It excoriated individual selfishness and extolled the virtues of brotherhood, kindness, and generosity at Christmas. ... Dickens preached that at Christmas men should forget self and think of others, especially the poor and the unfortunate." The message was one that both religious and secular people could endorse.
- ^ Kelly, Richard Michael, ed. (2003). A Christmas Carol. Broadview Press. pp. 9, 12. ISBN978-1-55111-476-7.
- ^ Cochrane, Robertson. Wordplay: origins, meanings, and usage of the English language. University of Toronto Press, 1996, p. 126, ISBN 0-8020-7752-8.
- ^ Hutton, Ronald, The Stations of the Sun: The Ritual Year in England. 1996. Oxford: Oxford University Press, p. 113. ISBN 0-19-285448-8.
- ^ Joe L. Wheeler. Christmas in My Heart, Volume 10, p. 97. Review and Herald Pub Assoc, 2001. ISBN 0-8280-1622-4.
- ^ Earnshaw, Iris (November 2003). "The History of Christmas Cards". Inverloch Historical Society Inc. Archived from the original on May 26, 2016. Retrieved July 25, 2008.
- ^ The Girlhood of Queen Victoria: a selection from Her Majesty's diaries, p. 61. Longmans, Green & Co., 1912. University of Wisconsin.
- ^ Lejeune, Marie Claire. Compendium of symbolic and ritual plants in Europe, p.550. University of Michigan ISBN 90-77135-04-9.
- ^ a b Shoemaker, Alfred Lewis. (1959) Christmas in Pennsylvania: a folk-cultural study. Edition 40. pp. 52, 53. Stackpole Books 1999. ISBN 0-8117-0328-2.
- ^ Godey's Lady's Book, 1850. Godey's copied it exactly, except he removed the Queen's tiara, and Prince Albert's moustache, to remake the engraving into an American scene.
- ^ Kelly, Richard Michael (ed.) (2003), A Christmas Carol, p. 20. Broadview Literary Texts, New York: Broadview Press, ISBN 1-55111-476-3.
- ^ Moore's poem transferred the genuine old Dutch traditions celebrated at New Year in New York, including the exchange of gifts, family feasting, and tales of "sinterklass" (a derivation in Dutch from "Saint Nicholas", from whence comes the modern "Santa Claus") to Christmas.The history of Christmas: Christmas history in America Archived April 19, 2018, at the Wayback Machine, 2006.
- ^ "Americans Celebrate Christmas in Diverse Ways" Archived December 10, 2006, at the Wayback Machine, Usinfo.state.gov, November 26, 2006.
- ^ First Presbyterian Church of Watertown "Oh ... and one more thing" December 11, 2005 Archived February 25, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b c Restad, Penne L. (1995), Christmas in America: a History, Oxford: Oxford University Press, p. 96. ISBN 0-19-510980-5.
- ^ "Christian church of God – history of Christmas". Christianchurchofgod.com. Archived from the original on December 19, 2010. Retrieved February 24, 2011.
- ^ Meggs, Philip B. A History of Graphic Design. 1998 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. p 148 ISBN 0-471-29198-6.
- ^ Jacob R. Straus (November 16, 2012). "Federal Holidays: Evolution and Current Practices" (PDF). Congressional Research Service. Archived (PDF) from the original on January 3, 2014. Retrieved January 2, 2014.
- ^ Weightman, Gavin; Humphries, Steve (1987). Christmas Past . London: Sidgwick and Jackson. p. 31.
- ^ Harding, Patrick (2003). The Xmas Files: Facts Behind the Myths and Magic of Christmas. London: Metro Publishing.
- ^ "When was the last time football matches in Britain were played on Christmas Day?". The Guardian. Archived from the original on October 6, 2014. Retrieved October 23, 2014.
- ^ Connelly, Mark (2000). Christmas at the Movies: Images of Christmas in American, British and European Cinema. I.B.Tauris. p. 186. ISBN978-1-86064-397-2.
A chapter on representations of Christmas in Soviet cinema could, in fact be the shortest in this collection: suffice it to say that there were, at least officially, no Christmas celebrations in the atheist socialist state after its foundation in 1917.
- ^ Ramet, Sabrina Petra (November 10, 2005). Religious Policy in the Soviet Union. Cambridge University Press. p. 138. ISBN978-0-521-02230-9.
The League sallied forth to save the day from this putative religious revival. Antireligioznik obliged with so many articles that it devoted an entire section of its annual index for 1928 to anti-religious training in the schools. More such material followed in 1929, and a flood of it the next year. It recommended what Lenin and others earlier had explicitly condemned—carnivals, farces, and games to intimidate and purge the youth of religious belief. It suggested that pupils campaign against customs associated with Christmas (including Christmas trees) and Easter. Some schools, the League approvingly reported, staged an anti-religious day on the 31st of each month. Not teachers but the League's local set the programme for this special occasion.
- ^ Zugger, Christopher Lawrence (2001). Catholics of the Soviet Empire from Lenin Through Stalin. Syracuse University Press. p. 210. ISBN978-0-8156-0679-6.
As observed by Nicholas Brianchaninov, writing in 1929–1930, after the NEP and just as the worst of collectivization was beginning, the Soviets deemed it necessary to drive into the heads of the people the axiom that religion was the synthesis of everything most harmful to humanity. It must be presented as the enemy of man and society, of life and learning, of progress. ... In caricatures, articles, Bezbozhnik, Antireligioznik, League of Militant Atheists propaganda and films. School courses [were give] on conducting the struggle against religion (how to profane a church, break windows, objects of piety). The young, always eager to be with the latest trend, often responded to such propaganda. In Moscow in 1929 children were brought to spit on the crucifixes at Christmas. Priests in Tiraspol diocese were sometimes betrayed by their own young parishioners, leading to their imprisonment and even death, and tearing their families apart.
- ^ Goldberg, Carey (January 7, 1991). "A Russian Christmas—Better Late Than Never : Soviet Union: Orthodox Church celebration is the first under Communists. But, as with most of Yeltsin's pronouncements, the holiday stirs a controversy". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved November 22, 2014.
For the first time in more than seven decades, Christmas—celebrated today by Russian Orthodox Christians—is a full state holiday across Russia's vast and snowy expanse. As part of Russian Federation President Boris N. Yeltsin's ambitious plan to revive the traditions of Old Russia, the republic's legislature declared last month that Christmas, long ignored under atheist Communist ideology, should be written back into the public calendar. "The Bolsheviks replaced crosses with hammers and sickles," said Vyacheslav S. Polosin, head of the Russian legislature's committee on religion. "Now they are being changed back."
- ^ Perry, Joseph (December 24, 2015). "How the Nazis co-opted Christmas: A history of propaganda". The Washington Post. Archived from the original on January 6, 2016. Retrieved March 11, 2016.
- ^ "Somalia joins Brunei by banning Christmas celebrations 'to protect Islam'". The Daily Telegraph. December 24, 2015. Archived from the original on May 29, 2018. Retrieved April 4, 2018.
- ^ Jespersen, Knud J. V. (June 21, 2011). A History of Denmark. Macmillan International Higher Education. p. 91. ISBN9780230344174.
It is quite normal to go to church on Christmas Eve, and many people like to celebrate a christening or wedding in church. The Church is especially important at the end of a life; by far the majority of funerals are still conducted in a church by a minister.
- ^ "2018 Worship and Music Planning Calendar". The United Methodist Church. 2018. Retrieved December 9, 2018.
- ^ Stetzer, Ed (December 14, 2015). "What Is Church Attendance Like During Christmastime? New Data From LifeWay Research". Christianity Today. Archived from the original on January 29, 2018. Retrieved December 9, 2018.
- ^ Bingham, John (October 27, 2016). "British families only attend church at Christmas, new figures suggest". The Daily Telegraph. Archived from the original on December 27, 2017. Retrieved December 24, 2017.
- ^ Collins, Ace, Stories Behind the Great Traditions of Christmas, Zondervan, (2003), ISBN 0-310-24880-9 p.47.
- ^ Internet Archive Susan Topp Weber, Nativities of the World, Gibbs Smith, 2013
- ^ "Alla scoperta dei cinque presepi più belli di Bologna | Nuok". Nuok.it. January 24, 2013. Archived from the original on December 27, 2013. Retrieved December 25, 2013.
- ^ "Presepi in Liguria: provincia di Genova, Tigullio -sito di Paolino". Digilander.libero.it. Archived from the original on December 27, 2013. Retrieved December 25, 2013.
- ^ "Holidays at the Museums : Carnegie Museum of Natural History". Carnegiemnh.org. November 26, 2013. Archived from the original on December 27, 2013. Retrieved December 25, 2013.
- ^ Bershad, David; Carolina Mangone, The Christian Travelers Guide to Italy, Zondervan, 2001.
- ^ "The Provençal Nativity Scene". Simplytreasures.com. Archived from the original on September 14, 2012. Retrieved December 25, 2013.
- ^ Seaburg, Carl, Celebrating Christmas: An Anthology, iUniverse, 2003.
- ^ Bowler, Gerry, The World Encyclopedia of Christmas, Random House LLC, 2012.
- ^ Carol King (December 24, 2012). "A Christmas Living Nativity Scene in Sicily". Italy Magazine. Archived from the original on December 26, 2013. Retrieved December 25, 2013.
- ^ Collins p. 83.
- ^ Nowak, Claire (December 23, 2019). "The Real Reason Why Christmas Colors Are Green and Red". Reader's Digest . Retrieved December 18, 2020.
- ^ Norris, Rebecca (October 29, 2019). "Here's the History Behind Why Red and Green Are the Traditional Christmas Colors". Country Living . Retrieved December 18, 2020.
- ^ Collins, Ace (April 1, 2010). Stories Behind the Great Traditions of Christmas. Zondervan. ISBN978-0-310-87388-4 . Retrieved December 2, 2010.
- ^ Senn, Frank C. (2012). Introduction to Christian Liturgy. Fortress Press. p. 118. ISBN9781451424331.
The Christmas tree as we know it seemed to emerge in Lutheran lands in Germany in the sixteenth century. Although no specific city or town has been identified as the first to have a Christmas tree, records for the Cathedral of Strassburg indicate that a Christmas tree was set up in that church in 1539 during Martin Bucer's superintendency.
- ^ "The Christmas Tree". Lutheran Spokesman. 29–32. 1936.
The Christmas tree became a widespread custom among German Lutherans by the eighteenth century.
- ^ Kelly, Joseph F. (2010). The Feast of Christmas. Liturgical Press. p. 94. ISBN9780814639320.
German Lutherans brought the decorated Christmas tree with them; the Moravians put lighted candles on those trees.
- ^ Blainey, Geoffrey (October 24, 2013). A Short History of Christianity. Rowman & Littlefield Publishers. p. 418. ISBN9781442225909.
Many Lutherans continued to set up a small fir tree as their Christmas tree, and it must have been a seasonal sight in Bach's Leipzig at a time when it was virtually unknown in England, and little known in those farmlands of North America where Lutheran immigrants congregated.
- ^ Mandryk, DeeAnn (October 25, 2005). Canadian Christmas Traditions. James Lorimer & Company. p. 67. ISBN9781554390984.
The eight-pointed star became a popular manufactured Christmas ornament around the 1840s and many people place a star on the top of their Christmas tree to represent the Star of Bethlehem.
- ^ Wells, Dorothy (1897). "Christmas in Other Lands". The School Journal. 55: 697–8.
Christmas is the occasional of family reunions. Grandmother always has the place of honor. As the time approaches for enjoying the tree, she gathers her grandchildren about her, to tell them the story of the Christ child, with the meaning of the Christ child, with the meaning of the Christmas tree; how the evergreen is meant to represent the life everlasting, the candle lights to recall the light of the world, and the star at the top of the tree is to remind them of the star of Bethlehem.
- ^ Jones, David Albert (October 27, 2011). Angels. Oxford University Press. p. 24. ISBN9780191614910.
The same ambiguity is seen in that most familiar of angels, the angel on top of the Christmas tree. This decoration, popularized in the nineteenth century, recalls the place of the angels in the Christmas story (Luke 2.9–18).
- ^ a b van Renterghem, Tony. When Santa was a shaman. St. Paul: Llewellyn Publications, 1995. ISBN 1-56718-765-X.
- ^ Fritz Allhoff, Scott C. Lowe (2010). Christmas. John Wiley & Sons.
His biographer, Eddius Stephanus, relates that while Boniface was serving as a missionary near Geismar, Germany, he had enough of the locals' reverence for the old gods. Taking an axe to an oak tree dedicated to Norse god Thor, Boniface chopped the tree down and dared Thor to zap him for it. When nothing happened, Boniface pointed out a young fir tree amid the roots of the oak and explained how this tree was a more fitting object of reverence as it pointed towards the Christian heaven and its triangular shape was reminiscent of the Christian trinity.
- ^ Harper, Douglas, Christ Archived May 9, 2006, at the Wayback Machine, Online Etymology Dictionary, 2001.
- ^ "The Chronological History of the Christmas Tree". The Christmas Archives. Archived from the original on December 21, 2007. Retrieved December 18, 2007.
- ^ "Christmas Tradition – The Christmas Tree Custom". Fashion Era. Archived from the original on December 18, 2007. Retrieved December 18, 2007.
- ^ Hewitson, Carolyn (2013). Festivals. Routledge. ISBN9781135057060.
It is said to resemble the star of Bethlehem. The Mexicans call it the flower of the Holy Night, but usually it is called poinsettia after the man who introduced it to America, Dr Joel Poinsett.
- ^ "The Legends and Traditions of Holiday Plants". www.ipm.iastate.edu. Archived from the original on January 22, 2016. Retrieved February 17, 2016.
- ^ "StackPath". www.gardeningknowhow.com . Retrieved December 23, 2020.
- ^ "Germany's Advent wreath tradition, and how to make one of your own". Stripes Europe. November 21, 2019. Retrieved December 23, 2020.
- ^ "Liturgical Year : Symbolic Lights and Fires of Christmas (Activity)". Catholic Culture. Archived from the original on January 13, 2012. Retrieved December 10, 2011.
- ^ Murray, Brian. "Christmas lights and community building in America," History Matters, Spring 2006. Archived June 29, 2010, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Epiphany: Should Christmas decorations come down on 6 January?". BBC News. January 6, 2017. Retrieved December 23, 2020.
- ^ a b c d e Collins, Ace (2010). Stories Behind the Great Traditions of Christmas. Zondervan. pp. 139–141. ISBN9780310873884.
- ^ Miles, Clement, Christmas customs and traditions, Courier Dover Publications, 1976, ISBN 0-486-23354-5, p. 32.
- ^ Dudley-Smith, Timothy (1987). A Flame of Love. London: Triangle/SPCK. ISBN978-0-281-04300-2.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Smolko, Joanna (February 4, 2012). "Christmas music". Grove Music Online. Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/gmo/9781561592630.article.A2227990.
- ^ Broomfield, Andrea (2007), Food and Cooking in Victorian England: A History, Greenwood Publishing Group, 2007, pp. 149–150.
- ^ Muir, Frank (1977), Christmas customs & traditions, Taplinger Pub. Co., 1977, p. 58.
- ^ "Carp for Christmas: the odd Central European tradition explained". Kafkadesk. December 9, 2018.
- ^ "Christmas card sold for record price" Archived February 5, 2006, at the Wayback Machine, BBC News. Retrieved October 28, 2011.
- ^ Schaverien, Anna (June 19, 2021). "E-Cards Are Back, Thanks to the Pandemic". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved November 13, 2021.
- ^ "It's time to mail your holiday cards — if you can find any". NBC News . Retrieved November 13, 2021.
- ^ Pruitt, Sarah. "The War of Words behind 'Happy Holidays'". HISTORY . Retrieved December 24, 2020.
- ^ Collins, Ace (April 20, 2010). Stories Behind the Great Traditions of Christmas. Zondervan. p. 17. ISBN9780310873884 . Retrieved April 10, 2012.
The legend of St. Nicholas, who became the bishop of Myra in the beginning of the fourth century, is the next link in the Christmas-gift chain. Legend has it that during his life the priest rode across Asia Minor bestowing gifts upon poor children.
- ^ Trexler, Richard (May 23, 1997). The Journey of the Magi: Meanings in History of a Christian Story. Princeton University Press. p. 17. ISBN978-0691011264. Archived from the original on December 31, 2015. Retrieved April 10, 2012.
This exchange network of ceremonial welcome was mirrored in a second reciprocity allowing early Christians to imagine their own magi: the phenomenon of giving gifts.
- ^ Collins, Ace (April 20, 2010). Stories Behind the Great Traditions of Christmas. Zondervan. p. 17. ISBN9780310873884 . Retrieved April 10, 2012.
Most people today trace the practice of giving gifts on Christmas Day to the three gifts that the Magi gave to Jesus.
- ^ Berking, Helmuth (March 30, 1999). Sociology of Giving. SAGE Publications. p. 14. ISBN978-0-85702-613-2.
For the Enlightenment educationalist, gift-giving turned out to be a relic of a pagan custom, namely, the Roman Saturnalia. After the introduction of the Julian calendar in Rome, the 25th of December became the day of Sol invictus when people greeted the winter solstice. It was the day of the Sun's rebirth, and it was the day of the Christmas festivities – although it was only in the year 336 AD that it appears to have become established as the day of Jesus's birth (see Pannenberg 1989: 57). The Eastern Church adopted this date even later, towards the end of the 4th century, having previously regarded the 6th of January as the day of gift-giving, as it still is in the Italian community of Befana. The winter solstice was a time of festivity in every traditional culture, and the Christian Christmas probably took its place within this mythical context of the solar cult. Its core dogma of the Incarnation, however, solidly established the giving and receiving of gifts as the structural principle of that recurrent yet unique event. 'Children were given presents as the Jesus child received gifts from the magi or kings who came from afar to adore him. But in reality it was they, together with all their fellow men, who received the gift of God through man's renewed participation in the divine life' (ibid.: 61).
- ^ Seward, Pat; Lal, Sunandini Arora (2006). Netherlands. Marshall Cavendish. p. 116. ISBN978-0-7614-2052-1.
Until quite recently, the celebrations focused solely on Saint Nicholas, or Sinterklaas (SIN-ter-klahs), as the Dutch call him. ... Interestingly, the American Santa Claus was born out of the Dutch Sinterklaas.
- ^ Domenico, Roy Palmer (2002). The regions of Italy: a reference guide to history and culture. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 21. ISBN978-0-313-30733-1.
Saint Nicholas (Bishop of Myra) replaced Sabino as the patron saint of the city... A Greek from what is now Turkey, he lived in the early fourth century.
- ^ Collins, Ace (2009). Stories Behind Men of Faith . Zondervan. p. 121. ISBN978-0-310-56456-0 . Retrieved June 20, 2015.
Nicholas was born in the Greek city of Patara around 270 AD. The son of a businessman named Theophanes and his wife, Nonna, the child's earliest years were spent in Myra... As a port on the Mediterranean Sea, in the middle of the sea lanes that linked Egypt, Greece and Rome, Myra was a destination for traders, fishermen, and merchant sailors. Spawned by the spirit of both the city's Greek heritage and the ruling Roman government, cultural endeavors such as art, drama, and music were mainstays of everyday life.
- ^ Jona Lendering (November 20, 2008). "Saint Nicholas, Sinterklaas, Santa Claus". Livius.org. Archived from the original on May 13, 2011. Retrieved February 24, 2011.
- ^ "St. Basil (330–379)". Skiathosbooks.com. Archived from the original on January 12, 2012. Retrieved February 3, 2012.
- ^ Matera, Mariane. "Santa: The First Great Lie" Archived September 14, 2007, at the Wayback Machine, Citybeat, Issue 304.
- ^ "Kto przynosi Wam prezenty? Św. Mikołaj, Gwiazdor, Aniołek, Dzieciątko czy może Dziadek Mróz?". Bezprawnik (in Polish). December 22, 2016. Archived from the original on December 24, 2017. Retrieved December 24, 2017.
- ^ "Nie tylko Mikołaj, czyli kto według tradycji rozdaje prezenty w różnych regionach Polski?". gazeta.pl (in Polish). Archived from the original on December 24, 2017. Retrieved December 24, 2017.
- ^ "Christmas in Bethlehem". www.sacred-destinations.com. Archived from the original on June 16, 2010. Retrieved June 12, 2010.
- ^ Siegbert Uhlig, Encyclopaedia Aethiopica He-N, p. 538
- ^ Varga, Melody. "Black Friday, About:Retail Industry. Archived May 17, 2008, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Definition Christmas Creep – What is Christmas Creep". Womeninbusiness.about.com. November 2, 2010. Archived from the original on December 27, 2010. Retrieved February 24, 2011.
- ^ "South Molton and Brook Street Christmas Lights" Archived November 19, 2010, at the Wayback Machine (November 16, 2010), View London.co.uk.
- ^ a b Kollewe, Julia, (November 29, 2010), "West End spree worth £250m marks start of Christmas shopping season" Archived December 21, 2016, at the Wayback Machine, The Guardian.
- ^ Gwen Outen (December 3, 2004). "ECONOMICS REPORT – Holiday Shopping Season in the U.S." Voice of America. Archived from the original on March 3, 2009.
- ^ US Census Bureau. "Facts. The Holiday Season" December 19, 2005. (accessed November 30, 2009) Archived copy at the Library of Congress (May 7, 2010).
- ^ US Census 2005.
- ^ Haury, Amanda C. (November 8, 2019). "Average Cost of an American Christmas". Investopedia. Dotdash. Retrieved December 17, 2019.
- ^ Zauzmer, Ben (January 31, 2020). "Oscar Seasons: The Intersection of Data and the Academy Awards". Harvard Data Science Review. 2 (1). doi:10.1162/99608f92.6230ce9f. Retrieved November 15, 2021.
- ^ "The Deadweight Loss of Christmas", American Economic Review, December 1993, 83 (5).
- ^ "Is Santa a deadweight loss?" Archived December 21, 2005, at the Wayback Machine The Economist December 20, 2001.
- ^ Reuters. "Christmas is Damaging the Environment, Report Says" Archived March 12, 2007, at the Wayback Machine, December 16, 2005.
- ^ Harper, Timothy (1999). Moscow Madness: Crime, Corruption, and One Man's Pursuit of Profit in the New Russia . McGraw-Hill. p. 72. ISBN9780070267008.
- ^ "Marta Patiño, The Puritan Ban on Christmas". Timetravel-britain.com. Archived from the original on March 1, 2011. Retrieved February 24, 2011.
- ^ Christmas in the Colonies Archived December 25, 2011, at the Wayback Machine Time. Retrieved December 25, 2011.
- ^ Todd, Margo (2002). The Culture of Protestantism in Early Modern Scotland. Yale University Press. p. 187. ISBN978-0-300-09234-9.
- ^ Goldberg, Carey (January 7, 1991). "A Russian Christmas—Better Late Than Never : Soviet Union: Orthodox Church Celebration Is the First Under Communists. But, as with Most of Yeltsin's Pronouncements, the Holiday Stirs a Controversy". Los Angeles Times. Archived from the original on December 22, 2015. Retrieved August 11, 2016.
- ^ Woolf, Nicky (December 24, 2015). "Christmas celebrations banned in Somalia, Tajikistan and Brunei". The Guardian. Archived from the original on August 26, 2016. Retrieved August 10, 2016.
- ^ "ACLJ, Christmas laws". Aclj.org. Archived from the original on December 25, 2013. Retrieved December 25, 2013.
- ^ Christmas controversy article – Muslim Canadian Congress. [ dead link ]
- ^ Feder, Don, "In the culture, Christmas morphs into holiday" Archived April 12, 2010, at the Wayback Machine, Jewish World Review, December 13, 2000.
- ^ "The Brits Have It Right: Forget Happy Holidays, Just Wish People Merry Christmas". The Guardian. London. August 11, 2016. Archived from the original on December 21, 2016. Retrieved December 11, 2016.
- ^ Jankowski, Paul (August 11, 2016). "Is Saying 'Merry Christmas' Politically Correct? Who Cares?". Forbes. Archived from the original on August 7, 2017. Retrieved August 22, 2017.
- ^ "If We Can't Say 'Merry Christmas' in Canada, Multiculturalism Failed". HuffPost. August 11, 2016. Archived from the original on September 29, 2016. Retrieved August 11, 2016.
- ^ "Lynch vs. Donnelly". Belcherfoundation.org. 1984. Archived from the original on February 16, 2006. Retrieved April 12, 2006.
- ^ Mujahid, Abdul Malik. "Treating Christmas with respect Archived April 5, 2017, at the Wayback Machine," Sound Vision.
- ^ Dillon, Michael (2001). Religious Minorities and China. Minority Rights Group International.
- ^ Buang, Sa'eda; Chew, Phyllis Ghim-Lian (May 9, 2014). Muslim Education in the 21st Century: Asian Perspectives. Routledge. p. 75. ISBN9781317815006.
Subsequently, a new China was found on the basis of Communist ideology, i.e. atheism. Within the framework of this ideology, religion was treated as a 'contorted' world-view and people believed that religion would necessarily disappear at the end, along with the development of human society. A series of anti-religious campaigns was implemented by the Chinese Communist Party from the early 1950s to the late 1970s. As a result, in nearly 30 years between the beginning of the 1950s and the end of the 1970s, mosques (as well as churches and Chinese temples) were shut down and Imams involved in forced 're-education'.
- ^ "Alarm over China's Church crackdown". BBC. December 18, 2018. Archived from the original on January 5, 2019. Retrieved January 11, 2019.
Among those arrested are a prominent pastor and his wife, of the Early Rain Covenant Church in Sichuan. Both have been charged with state subversion. And on Saturday morning, dozens of police raided a children's Bible class at Rongguili Church in Guangzhou. One Christian in Chengdu told the BBC: "I'm lucky they haven't found me yet." China is officially atheist, though says it allows religious freedom.
- ^ "Santa Claus won't be coming to this town, as Chinese officials ban Christmas". South China Morning Post. December 18, 2018. Archived from the original on January 12, 2019. Retrieved January 11, 2019.
Christmas is not a recognised holiday in mainland China – where the ruling party is officially atheist – and for many years authorities have taken a tough stance on anyone who celebrates it in public. ... The statement by Langfang officials said that anyone caught selling Christmas trees, wreaths, stockings or Santa Claus figures in the city would be punished. ... While the ban on the sale of Christmas goods might appear to be directed at retailers, it also comes amid a crackdown on Christians practising their religion across the country. On Saturday morning, more than 60 police officers and officials stormed a children's Bible class in Guangzhou, capital of southern China's Guangdong province. The incident came after authorities shut down the 1,500-member Zion Church in Beijing in September and Chengdu's 500-member Early Rain Covenant Church last week. In the case of the latter, about 100 worshippers were snatched from their homes or from the streets in coordinated raids.
Further reading
- Bowler, Gerry, The World Encyclopedia of Christmas (October 2004: McClelland & Stewart). ISBN 978-0-7710-1535-9
- Bowler, Gerry, Santa Claus: A Biography (November 2007: McClelland & Stewart). ISBN 978-0-7710-1668-4
- Comfort, David, Just Say Noel: A History of Christmas from the Nativity to the Nineties (November 1995: Fireside). ISBN 978-0-684-80057-8
- Count, Earl W., 4000 Years of Christmas: A Gift from the Ages (November 1997: Ulysses Press). ISBN 978-1-56975-087-2
- Federer, William J., There Really Is a Santa Claus: The History of St. Nicholas & Christmas Holiday Traditions (December 2002: Amerisearch). ISBN 978-0-9653557-4-2
- Kelly, Joseph F., The Origins of Christmas (August 2004: Liturgical Press). ISBN 978-0-8146-2984-0
- Miles, Clement A., Christmas Customs and Traditions (1976: Dover Publications). ISBN 978-0-486-23354-3
- Nissenbaum, Stephen, The Battle for Christmas (1996; New York: Vintage Books, 1997). ISBN 0-679-74038-4
- Restad, Penne L. (1995). Christmas in America: A History . New York: Oxford University Press. ISBN978-0-19-509300-1.
- Rosenthal, Jim, St. Nicholas: A Closer Look at Christmas (July 2006: Nelson Reference). ISBN 1-4185-0407-6
- Sammons, Peter (May 2006). The Birth of Christ. Glory to Glory Publications (UK). ISBN978-0-9551790-1-3.
- "Christmas". Encyclopædia Britannica. 6 (11th ed.). 1911. pp. 293–294.
External links
- Christmas: Its Origin and Associations, by William Francis Dawson, 1902, from Project Gutenberg
What Does the Word Christmas Mean Broken Down
Source: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Christmas
0 Response to "What Does the Word Christmas Mean Broken Down"
Post a Comment